リソース定義@Istio¶
はじめに¶
本サイトにつきまして、以下をご認識のほど宜しくお願いいたします。
01. 全部入りセットアップ¶
インストール¶
▼ チャートとして¶
チャートリポジトリからチャートをインストールし、Kubernetesリソースを作成する。
チャートは、istioctl コマンドインストール時、manifests ディレクトリ以下に同梱される。
# IstioOperatorのdemoをインストールし、リソースを作成する
$ istioctl install --set profile=demo revision=1-10-0
# 外部のチャートを使用する場合
$ istioctl install --manifests=foo-chart
執筆時点 (2023/01/16) でIstioOperatorは非推奨になっている。
▼ Operatorとして (ユーザー定義)¶
プロファイルを使用する代わりに、IstioOperatorを自前で定義しても良い。
# istio-operator.yamlファイル
apiVersion: install.istio.io/v1alpha1
kind: IstioOperator
metadata:
name: istio-operator
spec:
# Istioのdemoチャートをインストールし、リソースを作成する。
profile: demo
$ kubectl apply -f istio-operator.yaml
ローカルマシンのセットアップ¶
▼ Minikube¶
Istioによる種々のコンテナが稼働するために、MinikubeのNodeのCPUとメモリを最低サイズを以下の通りにする必要がある。
$ minikube start --cpus=4 --memory=16384
01-02. コンポーネント別セットアップ¶
インストール¶
▼ Google-APIsから¶
Google-APIsから、Istioのコンポーネント別にチャートをインストールし、リソースを作成する。
$ helm repo add <チャートリポジトリ名> https://istio-release.storage.googleapis.com/charts
$ helm repo update
$ kubectl create namespace istio-system
# baseチャート
$ helm install <Helmリリース名> <チャートリポジトリ名>/base -n istio-system --version <バージョンタグ>
# Istiodコントロールプレーンのみ
# istiodチャート
$ helm install <Helmリリース名> <チャートリポジトリ名>/istiod -n istio-system --version <バージョンタグ>
IngressGatewayのインストールは必須でない。
# IngressGatewayのみ
# gatewayチャート
$ helm install <Helmリリース名> <チャートリポジトリ名>/gateway -n istio-system --version <バージョンタグ>
02. AuthorizationPolicy¶
.metadata.namespace¶
AuthorizationPolicyの適用範囲の仕組みは、RequestAuthenticationと同じである。
作成したNamespaceに対して適用され、istio-system に置いた場合は全てのNamespaceに適用される。
もし、適用範囲を小さくしたい場合は、.spec.selector キーを使用する。
.spec.action¶
▼ actionとは¶
認可スコープで、認証済みの送信元を許可するか否かを設定する。
apiVersion: security.istio.io/v1
kind: AuthorizationPolicy
metadata:
name: bar-authorization-policy
spec:
action: ALLOW
.spec.provider¶
▼ providerとは¶
認可フェーズの委譲先のIDプロバイダーを設定する。
事前に、ConfigMapの .mesh.extensionProvider キーにIDプロバイダーを登録しておく必要がある。
*実装例*
ここでは、OAuth2 ProxyをIDプロバイダーとして使用する。
apiVersion: security.istio.io/v1
kind: AuthorizationPolicy
metadata:
name: oauth2-proxy-authorization-policy
spec:
action: CUSTOM
provider:
name: oauth2-proxy
rules:
- to:
- operation:
paths: ["/login"]
OAuth2 ProxyのPodに紐づくServiceを識別できるようにする。
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: istio-mesh-cm
data:
mesh: |
extensionProviders:
- name: oauth2-proxy
envoyExtAuthzHttp:
service: oauth2-proxy.auth.svc.cluster.local
port: 80
includeHeadersInCheck:
- cookie
- authorization
- https://zenn.dev/takitake/articles/a91ea116cabe3c#istio%E3%81%AB%E5%A4%96%E9%83%A8%E8%AA%8D%E5%8F%AF%E3%82%B5%E3%83%BC%E3%83%90%E3%83%BC%E3%82%92%E7%99%BB%E9%8C%B2
- https://zenn.dev/takitake/articles/a91ea116cabe3c#%E5%BF%85%E8%A6%81%E3%81%AA%E3%83%AA%E3%82%BD%E3%83%BC%E3%82%B9%E3%82%92%E4%BD%9C%E6%88%90-1
- https://istio.io/latest/docs/tasks/security/authorization/authz-custom/#define-the-external-authorizer
.spec.rules¶
▼ rulesとは¶
認可スコープで、実施条件 (例:いずれのKubernetesリソース、HTTPメソッド、JWTトークンの発行元IDプロバイダーの識別子) を設定する。
その条件に合致した場合、認証済みの送信元を許可するか否かを実施する。
▼ 特定のServiceAccountを持つPodを送信元として許可する¶
送信元Podに紐づくServiceAccountが送信元の場合、認可を実施する。
Istioはクライアント証明書にID (例:SPIFEE ID) を設定しており、このIDが principals 値と一致するかを検証する。
Kubernetesでは送信元Podの名前を知る方法がない (IPアドレスは可能) なので、制御しやすくなる。
*実装例*
apiVersion: security.istio.io/v1
kind: AuthorizationPolicy
metadata:
name: allow-pod
spec:
rules:
- from:
- source:
principals: ["cluster.local/ns/default/sa/inventory-sa"]
to:
- operation:
methods: ["GET"]
▼ 特定のNamespaceを送信元として許可する¶
特定のNamespaceが送信元の場合、認可を実施する。
apiVersion: security.istio.io/v1
kind: AuthorizationPolicy
metadata:
name: allow-namespace
spec:
rules:
- from:
- source:
namespaces: ["foo"]
to:
- operation:
methods: ["GET"]
▼ 正しいJWTを許可する¶
リクエストヘッダーにあるJWTトークンの発行元IDプロバイダーが適切な場合、認可を実施するように設定する。
*実装例*
apiVersion: security.istio.io/v1
kind: AuthorizationPolicy
metadata:
name: allow-jwt
spec:
# 許可する
action: ALLOW
rules:
- when:
- key: request.auth.claims[iss]
# JWTトークンがある場合にのみ許可する
values: ["<JWTトークンの発行元IDプロバイダーの識別子 (issuer)>"]
*実装例*
apiVersion: security.istio.io/v1
kind: AuthorizationPolicy
metadata:
name: allow-jwt
spec:
# 許可する
action: ALLOW
rules:
# fromを設定しない場合、指定したパスではJWTトークンがなくても許可する
- to:
- operation:
paths:
- /
- /callback*
- /login
- /logout
- /static*
▼ 全てを拒否する¶
apiVersion: security.istio.io/v1
kind: AuthorizationPolicy
metadata:
name: deny-all
spec:
action: DENY
rules:
- {}
▼ 全てを許可する¶
apiVersion: security.istio.io/v1
kind: AuthorizationPolicy
metadata:
name: allow-all
spec:
action: ALLOW
rules:
- {}
▼ 非TLSを拒否する¶
apiVersion: security.istio.io/v1
kind: AuthorizationPolicy
metadata:
name: deny-non-tls
namespace: NAMESPACE
spec:
action: DENY
rules:
- from:
- source:
notPrincipals: ["*"]
.spec.selector¶
▼ selectorとは¶
AuthorizationPolicyの設定を適用するKubernetesリソースを設定する。
設定したKubernetesリソースに対して認証済みの送信元が通信した場合、AuthorizationPolicyを適用する。
apiVersion: security.istio.io/v1
kind: AuthorizationPolicy
metadata:
name: bar-authorization-policy
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: foo-pod
03. DestinationRule¶
.spec.exportTo¶
▼ exportToとは¶
そのDestinationRuleにリクエストできるNamespaceを設定する。
▼ * (アスタリスク)¶
デフォルト値である。
他のNamespaceのVirtualServiceに紐づける場合、* とする必要がある。
もし、同じNamespace内のVirtualServiceと紐づける場合、. とする。
つまり、Istio Ingress GatewayやIstio Egress Gatewayとリクエストを送受信するVirtualServiceとDestinationRuleでは * とし、それ以外のこれらの場合は . とする。
*実装例*
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
name: ingressgateway
spec:
exportTo:
- "*"
host: istio-inressgateway.istio-inress.svc.cluster.local
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
name: egressgateway
spec:
exportTo:
- "*"
host: istio-egressgateway.istio-egress.svc.cluster.local
▼ . (ドット)¶
同じNamespace内のVirtualServiceと紐づける場合、. とする。
もし、他のNamespaceのVirtualServiceに紐づける場合、* とする必要がある。
つまり、Istio Ingress GatewayやIstio Egress Gatewayとリクエストを送受信するVirtualServiceとDestinationRuleでは * とし、それ以外のこれらの場合は . とする。
*実装例*
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
name: foo-destination-rule
spec:
exportTo:
- "."
.spec.host¶
インバウンド通信のルーティング元とするServiceの名前を設定する。
これにより、Envoyは特定のServiceからのルーティングのみ受信するようになる。
*実装例*
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
name: foo-destination-rule
spec:
host: foo-service.default.svc.cluster.local # Service名でも良いが完全修飾ドメイン名のほうが良い。
*実装例*
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
name: egressgateway
spec:
exportTo:
- "*"
host: istio-egressgateway.istio-egress.svc.cluster.local
.spec.subsets¶
▼ subsetsとは¶
VirtualServiceを起点としたPodのカナリアリリースで使用する。
ルーティング先のPodの .metadata.labels キーを設定する。
.spec.subsets[*].name キーの値は、VirtualServiceで設定した .spec.http[*].route[*].destination.subset キーに合わせる必要がある。

*実装例*
subset が v1 に対するインバウンド通信では、version キーの値が v1 であるPodにルーティングする。
v2 も同様である。
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
name: foo-destination-rule
spec:
subsets:
- name: v1
labels:
version: v1 # 旧Pod
- name: v2
labels:
version: v2 # 新Pod
.spec.trafficPolicy¶
▼ connectionPool.http.maxRequestsPerConnection¶
1つのTCP接続で許可されるHTTP1.1とHTTP/2プロトコルのリクエストの最大数を設定する。
デフォルトでは上限がない。
2 以上であればTCP KeepAliveを実施する。1 とする場合はTCP KeepAliveを無効にする。
また、サーキットブレイカーを開始するための外れ値の閾値になる。
上限を超過した場合、Podへのルーティングが停止し、何らかの意図したエラーを返信する (サーキットブレイカー) 。
HTTP/2の場合は、TCP上で単一または複数のストリームを確立し、ストリーム内で単一または複数のリクエスト/レスポンスを並行的に送受信する。
そのため、リクエストの上限値を正確に検知することは難しく、おおよそになる。
*実装例*
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
name: foo-destination-rule
spec:
trafficPolicy:
connectionPool:
http:
# HTTP KeepAliveを無効にする
maxRequestsPerConnection: 1
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
name: foo-destination-rule
spec:
trafficPolicy:
connectionPool:
http:
maxRequestsPerConnection: 100
▼ connectionPool.http.http1MaxPendingRequests¶
キューに入れられるHTTPリクエストの最大数を設定する。
キューを超えるHTTPリクエストに対しては、503 レスポンスを返信する。
*実装例*
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
name: foo-destination-rule
spec:
trafficPolicy:
connectionPool:
http:
http1MaxPendingRequests: 4000
▼ connectionPool.http.http2MaxRequests¶
同時処理できるHTTP/1.1とHTTP/2の最大リクエスト数である。
これを超過した場合、そのリクエストに対しては 503 ステータスになる。
*実装例*
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
name: foo-destination-rule
spec:
trafficPolicy:
connectionPool:
http:
http2MaxRequests: 4000
▼ connectionPool.http.idleTimeout¶
HTTPリクエストでアイドルタイムアウト (パケットの送受信がない状態) を許可する時間を設定する。
不要な接続を早期に切断できる。
*実装例*
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
name: foo-destination-rule
spec:
trafficPolicy:
connectionPool:
http:
idleTimeout: 1000
▼ connectionPool.http.maxConcurrentStreams¶
同時に実行できるgRPCストリーミング処理の最大数である。
双方向ストリーミングRPCは同時ストリーミングであり、サーバーストリーミングRPCやクライアントストリーミングRPCも、非同期的に実行すれば同時ストリーミングになる。
*実装例*
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
name: foo-destination-rule
spec:
trafficPolicy:
connectionPool:
http:
maxConcurrentStreams: 1000
▼ connectionPool.tcp.connectTimeout¶
接続タイムアウト時間を設定する。
*実装例*
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
name: foo-destination-rule
spec:
trafficPolicy:
connectionPool:
tcp:
connectTimeout: 30ms
▼ connectionPool.tcp.idleTimeout¶
確立中のTCP接続でアイドルタイムアウト (パケットの送受信がない状態) を許可する時間を設定する。
不要な接続を早期に切断できる。
VirtualServiceの .spec.http.timeout キーとは異なり、DestinationRuleのアイドルタイムアウトはTCP接続中に無通信状態を許可する時間である。
*実装例*
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
name: foo-destination-rule
spec:
trafficPolicy:
connectionPool:
tcp:
idleTimeout: 1000
▼ connectionPool.tcp.tcpKeepalive¶
宛先との間でTCP KeepAliveを実施する。
*実装例*
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
name: foo-destination-rule
spec:
trafficPolicy:
connectionPool:
tcp:
tcpKeepalive:
probes: 9
time: 2
interval: 75
▼ connectionPool.tcp.maxConnections¶
キューに入れられるTCP接続の最大数を設定する。
*実装例*
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
name: foo-destination-rule
spec:
trafficPolicy:
connectionPool:
tcp:
maxConnections: 100
▼ outlierDetection.baseEjectionTime¶
オープン状態の期間を設定する。
baseEjectionTime キー後、宛先の正常性を確認し、もしエラー条件が発生していなければサーキットブレイカーを停止する。
もしエラー条件がまだ解決していなければ、もう一度 baseEjectionTime を実行する。
どのくらいの期間で10回以上を判定するかは、interval キーで設定する。
*実装例*
Gateway系ステータスが10秒間に10回以上発生したら、サーキットブレイカーを開始する。
サーキットブレイカー中に、異常なPodを30秒間排除する
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
name: foo-destination-rule
spec:
trafficPolicy:
outlierDetection:
consecutiveGatewayErrors: 10
interval: 10s
baseEjectionTime: 30s
- https://ibrahimhkoyuncu.medium.com/istio-powered-resilience-advanced-circuit-breaking-and-chaos-engineering-for-microservices-c3aefcb8d9a9
- https://speakerdeck.com/nutslove/istioru-men?slide=25
- https://ryo-koike.com/ja/blog/istio-advantages/#%E3%82%B5%E3%83%BC%E3%82%AD%E3%83%83%E3%83%88%E3%83%96%E3%83%AC%E3%83%BC%E3%82%AB%E3%83%BC
- https://istio.io/latest/docs/reference/config/networking/destination-rule/#OutlierDetection
▼ outlierDetection.consecutiveGatewayErrors¶
サーキットブレイカーを開始する外れ値 (Gateway系ステータスの 502、503、504) の閾値を設定する。
似た設定として、500 系ステータスの閾値を設定する consecutive5xxErrors キーがあるが、併用できる。
どのくらいの期間で10回以上を判定するかは、interval キーで設定する。
*実装例*
Gateway系ステータスが10秒間に10回以上発生したら、サーキットブレイカーを開始する。
サーキットブレイカー中に、異常なPodを30秒間排除する
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
name: foo-destination-rule
spec:
trafficPolicy:
outlierDetection:
consecutiveGatewayErrors: 10
interval: 10s
baseEjectionTime: 30s
- https://ibrahimhkoyuncu.medium.com/istio-powered-resilience-advanced-circuit-breaking-and-chaos-engineering-for-microservices-c3aefcb8d9a9
- https://speakerdeck.com/nutslove/istioru-men?slide=25
- https://istio.io/latest/docs/reference/config/networking/destination-rule/#OutlierDetection-consecutive_gateway_errors
▼ outlierDetection.consecutive5xxErrors¶
サーキットブレイカーを開始する外れ値 (500 系ステータス) の閾値を設定する。
似た設定として、Gateway系ステータス率の閾値を設定する consecutiveGatewayErrors キーがあるが、併用できる。
どのくらいの期間で10回以上を判定するかは、interval キーで設定する。
*実装例*
500 系ステータスが10秒間に10回以上発生したら、サーキットブレイカーを開始する。
サーキットブレイカー中に、異常なPodを30秒間排除する
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
name: foo-destination-rule
spec:
trafficPolicy:
outlierDetection:
consecutive5xxErrors: 10
interval: 10s
baseEjectionTime: 30s
▼ outlierDetection.interval¶
サーキットブレイカーの外れ値の計測間隔を設定する。
間隔内で閾値以上のエラーが発生した場合、サーキトブレイカーが起こる。
*実装例*
500 系ステータスが10秒間に10回以上発生したら、サーキットブレイカーを開始する。
サーキットブレイカー中に、異常なPodを30秒間排除する
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
name: foo-destination-rule
spec:
trafficPolicy:
outlierDetection:
consecutive5xxErrors: 10
interval: 10s
baseEjectionTime: 30s
▼ outlierDetection.maxEjectionPercent¶
Pod全体のうちで排除できる最大Pod数を設定する。
*実装例*
全てのPodを排除する。
代わりにistio-proxyから返却された 503 ステータス (response_flagは UH) のレスポンスに応じて、送信元マイクロサービスでフォールバックを実行する。
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
name: foo-destination-rule
spec:
trafficPolicy:
outlierDetection:
minHealthPercent: 90
interval: 10s
baseEjectionTime: 30s
maxEjectionPercent: 100
▼ outlierDetection.minHealthPercent¶
指定された割合で正常になるように、ルーティング先を決める。
異常なルーティング先がある場合は正常なほうにルーティングし、異常なルーティング先が回復することを待つ。
*実装例*
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
name: foo-destination-rule
spec:
trafficPolicy:
outlierDetection:
minHealthPercent: 90
interval: 10s
baseEjectionTime: 30s
▼ loadBalancer¶
Podへのルーティング時に使用する負荷分散方式を設定する。
*実装例*
複数のゾーンのPodに対して、ラウンドロビンでルーティングする。
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
name: foo-destination-rule
spec:
trafficPolicy:
loadBalancer:
# ラウンドロビン
simple: ROUND_ROBIN
*実装例*
指定したゾーンのPodに対して、指定した重みづけでルーティングする。
リージョン名やゾーン名は、Podの topology.kubernetes.io/region キーや topology.kubernetes.io/zone キーの値を設定する。
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
name: foo-destination-rule
spec:
trafficPolicy:
loadBalancer:
localityLbSetting:
enabled: "true"
distribute:
- from: <リージョン名>/<ゾーン名>/*
to:
"<リージョン名1>/<ゾーン名1>/*": 70
"<リージョン名2>/<ゾーン名2>/*": 30
*実装例*
複数のゾーンのPodに対して、最小リクエスト数でルーティングする。
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
name: foo-destination-rule
spec:
trafficPolicy:
loadBalancer:
# 最小リクエスト数
simple: LEAST_CONN
▼ portLevelSettings.loadBalancer¶
Podのポート番号別のルーティングの負荷分散方式を設定する。
*実装例*
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
name: foo-destination-rule
spec:
trafficPolicy:
portLevelSettings:
- loadBalancer:
simple: ROUND_ROBIN
▼ portLevelSettings.port¶
Podのポート番号別ルーティングで使用するポート番号を設定する。
*実装例*
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
name: foo-destination-rule
spec:
trafficPolicy:
portLevelSettings:
- port:
number: 80
▼ tls.mode¶
DestinationRuleと宛先 (特にサービスメッシュ外にある対象) の間の暗号化方式を設定する。
Gatewayにも似た設定があるが、あちらは送信元とGatewayの間の暗号化方式を設定する。
*実装例*
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
name: foo-destination-rule
spec:
trafficPolicy:
tls:
mode: DISABLE # 非TLS
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
name: foo-destination-rule
spec:
trafficPolicy:
tls:
mode: SIMPLE # TLS
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
name: foo-destination-rule
spec:
trafficPolicy:
tls:
mode: MUTUAL # 自己管理下の相互TLS認証
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
name: foo-destination-rule
spec:
trafficPolicy:
tls:
mode: ISTIO_MUTUAL # Istio管理下の相互TLS認証
▼ tls.clientCertificate¶
自己管理下の相互TLS認証 (MUTUAL) の場合、使用するサーバー証明書を設定する。
Istio管理下の相互TLS認証 (ISTIO_MUTUAL) の場合、Istiodコントロールプレーンは作成したSSL署名書を自動的に割り当てるので、設定不要である。
Namespace全体に同じ設定を適用する場合、PeerAuthenticationを使用する。
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
name: foo-destination-rule
spec:
trafficPolicy:
tls:
mode: MUTUAL
privateKey: /etc/certs/client_private_key.pem
▼ warmup.aggression¶
スロースタート方式 (通過させるリクエストの数を少しずつ増加させる) で、増加率を設定する。
1 の場合は、直線的に増加する。
リクエスト数の非常に多い高トラフィックなシステムで、起動直後のパフォーマンスが悪いアプリケーション (例:キャッシュに依存、接続プールの作成が必要、ウォームアップが必要なJVM言語製アプリケーション) にいきなり高負荷をかけないようにできる。
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
name: foo-destination-rule
spec:
trafficPolicy:
warmup:
duration: 30
aggression: 1
- https://istio.io/latest/docs/reference/config/networking/destination-rule/#LoadBalancerSettings-warmup
- https://istio.io/latest/docs/reference/config/networking/destination-rule/#WarmupConfiguration
- https://stackoverflow.com/a/75942527/12771072
- https://discuss.istio.io/t/need-help-setting-up-slow-start-in-kubernetes/16692
- https://www.envoyproxy.io/docs/envoy/latest/intro/arch_overview/upstream/load_balancing/slow_start
▼ warmup.duration¶
スロースタート方式 (通過させるリクエストの数を少しずつ増加させる) で、スロースタートの期間を設定する。
リクエスト数の非常に多い高トラフィックなシステムで、起動直後のパフォーマンスが悪いアプリケーション (例:キャッシュに依存、接続プールの作成が必要、ウォームアップが必要なJVM言語製アプリケーション) にいきなり高負荷をかけないようにできる。
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
name: foo-destination-rule
spec:
trafficPolicy:
warmup:
duration: 30
aggression: 1
- https://istio.io/latest/docs/reference/config/networking/destination-rule/#LoadBalancerSettings-warmup
- https://istio.io/latest/docs/reference/config/networking/destination-rule/#WarmupConfiguration
- https://discuss.istio.io/t/need-help-setting-up-slow-start-in-kubernetes/16692
- https://www.envoyproxy.io/docs/envoy/latest/intro/arch_overview/upstream/load_balancing/slow_start
04. EnvoyFilter¶
.spec.configPatches.applyTo¶
適用したいフィルター名を設定する。
*実装例*
ネットワークフィルターの設定値を変更する。
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: EnvoyFilter
metadata:
name: foo-envoy-filter
spec:
configPatches:
- applyTo: NETWORK_FILTER
*実装例*
ネットワークフィルターである network.http_connection_manager の設定値を変更する。
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: EnvoyFilter
metadata:
name: foo-envoy-filter
spec:
configPatches:
- applyTo: HTTP_FILTER
*実装例*
リスナーフィルターの設定値を変更する。
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: EnvoyFilter
metadata:
name: foo-envoy-filter
spec:
configPatches:
- applyTo: LISTENER_FILTER
.spec.configPatches.match¶
▼ matchとは¶
フィルターの設定値を変更する場合、その実行条件を設定する。
条件に合致する設定値があった場合、.spec.configPatches.patch キーで設定した内容の変更処理を実施する。
▼ cluster¶
指定したクラスターが存在する場合、フィルターの設定値を変更する。
*実装例*
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: EnvoyFilter
metadata:
name: foo-envoy-filter
spec:
configPatches:
- match:
cluster:
name: foo-cluster
▼ listener¶
指定したリスナーが存在する場合、フィルターの設定値を変更する。
*実装例*
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: EnvoyFilter
metadata:
name: foo-envoy-filter
spec:
configPatches:
- match:
listener:
filterChain:
filter:
name: envoy.filters.network.http_connection_manager
▼ context¶
指定したワークロードタイプ (例:istio-ingressgateway内のistio-proxy、istio-proxyコンテナのistio-proxy) の場合、フィルターの設定値を変更する。
*実装例*
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: EnvoyFilter
metadata:
name: foo-envoy-filter
spec:
configPatches:
- match:
# istio-ingressgatewayとistio-proxyコンテナの両方に適用する
- context: ANY
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: EnvoyFilter
metadata:
name: foo-envoy-filter
spec:
configPatches:
- match:
# istio-proxyコンテナのIngressリスナー後のフィルターに適用する
- context: SIDECAR_INBOUND
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: EnvoyFilter
metadata:
name: foo-envoy-filter
spec:
configPatches:
- match:
# istio-ingressgateway内のistio-proxyコンテナに適用する
- context: GATEWAY
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: EnvoyFilter
metadata:
name: foo-envoy-filter
spec:
configPatches:
- match:
# istio-proxyコンテナのアウトバウンド通信 (Egressリスナー後のフィルター)
- context: SIDECAR_OUTBOUND
.spec.configPatches.patch¶
▼ patchとは¶
.spec.configPatches.match キーに設定した設定値があった場合、フィルターの設定値の変更内容を設定する。
▼ operation¶
フィルターの設定値の変更方法を設定する。
*実装例*
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: EnvoyFilter
metadata:
name: foo-envoy-filter
spec:
configPatches:
- patch:
operation: MERGE
*実装例*
.spec.configPatches.match キーに合致したフィルターの直前に挿入する。
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: EnvoyFilter
metadata:
name: foo-envoy-filter
spec:
configPatches:
- patch:
operation: INSERT_BEFORE
*実装例*
フィルターの一番最初に挿入する。
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: EnvoyFilter
metadata:
name: foo-envoy-filter
spec:
configPatches:
- patch:
operation: INSERT_FIRST
*実装例*
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: EnvoyFilter
metadata:
name: foo-envoy-filter
spec:
configPatches:
- patch:
operation: MERGE
▼ value¶
既存のフィルターに適用したいフィルターを設定する。
*実装例*
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: EnvoyFilter
metadata:
name: foo-envoy-filter
spec:
configPatches:
- patch:
operation: MERGE
value:
name: envoy.filters.network.http_connection_manager
typed_config:
# ネットワークフィルター (http_connection_manager) を指定する
"@type": type.googleapis.com/envoy.extensions.filters.network.http_connection_manager.v3.HttpConnectionManager
.spec.configPatches.priority¶
フィルターの適用タイミングを設定する。
マイナス値の場合、デフォルトのフィルターよりも先に適用する。
*実装例*
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: EnvoyFilter
metadata:
name: foo-envoy-filter
spec:
priority: -1
04-02. EnvoyFilterのレートリミット¶
Istioのレートリミットとは¶
執筆時点で、Istioのトラフィック管理系リソースにはレートリミットの設定がない。
これはEnvoyFilterで設定する必要がある。
複数のistio-proxyにレートリミットを設定するグローバルレートリミットと、特定のものに設定するローカルレートリミットがある。
ローカルリミット¶
▼ 任意のリクエストに対して¶
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: EnvoyFilter
metadata:
name: filter-local-ratelimit-svc
namespace: istio-system
spec:
workloadSelector:
labels:
app: productpage
configPatches:
- applyTo: HTTP_FILTER
match:
# istio-proxyコンテナのインバウンド通信の処理に適用する
context: SIDECAR_INBOUND
# Listenerにレートリミットを設定する
listener:
filterChain:
filter:
name: "envoy.filters.network.http_connection_manager"
patch:
operation: INSERT_BEFORE
value:
name: envoy.filters.http.local_ratelimit
typed_config:
"@type": type.googleapis.com/udpa.type.v1.TypedStruct
type_url: type.googleapis.com/envoy.extensions.filters.http.local_ratelimit.v3.LocalRateLimit
value:
stat_prefix: http_local_rate_limiter
# 4秒中に4リクエスト数までを指定する
token_bucket:
max_tokens: 4
tokens_per_fill: 4
fill_interval: 60s
filter_enabled:
runtime_key: local_rate_limit_enabled
default_value:
numerator: 100
denominator: HUNDRED
filter_enforced:
runtime_key: local_rate_limit_enforced
default_value:
numerator: 100
denominator: HUNDRED
response_headers_to_add:
- append: false
header:
key: x-local-rate-limit
value: "true"
---
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: EnvoyFilter
metadata:
name: filter-local-ratelimit-svc
namespace: istio-system
spec:
workloadSelector:
labels:
app: productpage
configPatches:
- applyTo: HTTP_FILTER
match:
# istio-proxyコンテナのインバウンド通信の処理に適用する
context: SIDECAR_INBOUND
listener:
filterChain:
filter:
name: "envoy.filters.network.http_connection_manager"
patch:
operation: INSERT_BEFORE
value:
name: envoy.filters.http.local_ratelimit
typed_config:
"@type": type.googleapis.com/udpa.type.v1.TypedStruct
type_url: type.googleapis.com/envoy.extensions.filters.http.local_ratelimit.v3.LocalRateLimit
value:
stat_prefix: http_local_rate_limiter
- applyTo: HTTP_ROUTE
match:
# istio-proxyコンテナのインバウンド通信の処理に適用する
context: SIDECAR_INBOUND
routeConfiguration:
vhost:
name: "inbound|http|9080"
route:
action: ANY
patch:
operation: MERGE
value:
typed_per_filter_config:
envoy.filters.http.local_ratelimit:
"@type": type.googleapis.com/udpa.type.v1.TypedStruct
type_url: type.googleapis.com/envoy.extensions.filters.http.local_ratelimit.v3.LocalRateLimit
value:
stat_prefix: http_local_rate_limiter
# 4秒中に4リクエスト数までを指定する
token_bucket:
max_tokens: 4
tokens_per_fill: 4
fill_interval: 60s
filter_enabled:
runtime_key: local_rate_limit_enabled
default_value:
numerator: 100
denominator: HUNDRED
filter_enforced:
runtime_key: local_rate_limit_enforced
default_value:
numerator: 100
denominator: HUNDRED
response_headers_to_add:
- append: false
header:
key: x-local-rate-limit
value: "true"
▼ JWTの同じ sub に対して¶
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: EnvoyFilter
metadata:
name: ratelimit-by-jwt-sub
namespace: default
spec:
workloadSelector:
labels:
app: my-app
configPatches:
- applyTo: HTTP_FILTER
match:
context: SIDECAR_INBOUND
listener:
filterChain:
filter:
name: envoy.filters.network.http_connection_manager
patch:
operation: INSERT_BEFORE
value:
name: envoy.filters.http.ratelimit
typed_config:
"@type": type.googleapis.com/envoy.extensions.filters.http.ratelimit.v3.RateLimit
domain: mydomain
rate_limit_service:
grpc_service:
envoy_grpc:
cluster_name: rate_limit_cluster
timeout: 0.25s
rate_limit_config:
rate_limit_descriptor_sets:
descriptors:
- entries:
- key: "identified_user_daily_limit"
value: "%DYNAMIC_METADATA(envoy.filters.http.jwt_authn.jwt_payload.sub)%"
グローバルレートリミット¶
▼ グローバルレートリミットとは¶
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: ratelimit-config
data:
config.yaml: |
domain: ratelimit
descriptors:
- key: PATH
value: "/productpage"
rate_limit:
unit: minute
requests_per_unit: 1
- key: PATH
value: "api"
rate_limit:
unit: minute
requests_per_unit: 2
- key: PATH
rate_limit:
unit: minute
requests_per_unit: 100
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: EnvoyFilter
metadata:
name: filter-ratelimit
# サービスメッシュ全体に適用する
namespace: istio-system
spec:
workloadSelector:
labels:
# Istio Ingress Gatewayに合致させる
istio: ingressgateway
configPatches:
- applyTo: HTTP_FILTER
match:
# Gatewayの処理に適用する
context: GATEWAY
# Listenerにレートリミットを設定する
listener:
filterChain:
filter:
name: "envoy.filters.network.http_connection_manager"
subFilter:
name: "envoy.filters.http.router"
# 変更内容を設定する
patch:
operation: INSERT_BEFORE
value:
name: envoy.filters.http.ratelimit
typed_config:
"@type": type.googleapis.com/envoy.extensions.filters.http.ratelimit.v3.RateLimit
domain: ratelimit
# true:istio-proxyコンテナが失敗のレスポンスを返信する
# false:マイクロサービスが失敗のレスポンスを返信する
failure_mode_deny: true
timeout: 10s
rate_limit_service:
grpc_service:
envoy_grpc:
# レートリミットの対象を設定する
cluster_name: outbound|8081||ratelimit.default.svc.cluster.local
authority: ratelimit.default.svc.cluster.local
transport_api_version: V3
---
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: EnvoyFilter
metadata:
name: filter-ratelimit-svc
# サービスメッシュ全体に適用する
namespace: istio-system
spec:
workloadSelector:
labels:
istio: ingressgateway
configPatches:
- applyTo: VIRTUAL_HOST
match:
# Gatewayの処理に適用する
context: GATEWAY
routeConfiguration:
vhost:
name: ""
route:
action: ANY
# 変更内容を設定する
patch:
operation: MERGE
value:
rate_limits:
- actions:
- request_headers:
header_name: ":path"
descriptor_key: "PATH"
04-03. EnvoyFilterのKeepAliveの設定¶
istio-ingressgateway内のistio-proxyで、KeepAliveを実行できるようにする。
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: EnvoyFilter
metadata:
name: istio-ingressgateway
namespace: foo-namespace
spec:
configPatches:
- applyTo: LISTENER
match:
# istio-ingressgatewayのフィルターの設定値を変更する
context: GATEWAY
listener:
name: 0.0.0.0_8443
portNumber: 8443
# 変更内容を設定する
patch:
operation: MERGE
value:
socket_options:
- level: 1
name: 9
# KeepAliveを有効化する
int_value: 1
state: STATE_PREBIND
- level: 6
name: 4
# 15秒間の無通信が発生したら、KeepAliveを実行する
int_value: 15
state: STATE_PREBIND
- level: 6
name: 5
# 15秒間隔で、KeepAliveを実行する
int_value: 15
state: STATE_PREBIND
- level: 6
name: 6
# 10回応答がなければ終了する
int_value: 3
state: STATE_PREBIND
04-04. EnvoyFilter以外のカスタマイズ方法¶
VirtualService、DestinationRuleの定義¶
VirtualServiceとDestinationRuleの設定値は、istio-proxyに適用される。
annotationsの定義¶
DeploymentやPodの .metadata.anontations キーにて、istio-proxyごとのオプション値を設定する。
istio-proxyの定義¶
DeploymentやPodでistio-proxyを定義することにより設定を変更できる。
*実装例*
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: foo-deployment
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: foo-pod
template:
spec:
containers:
- name: app
image: app
# istio-proxyコンテナの設定を変更する。
- name: istio-proxy
lifecycle:
# istio-proxyコンテナ開始直後の処理
postStart:
exec:
# istio-proxyコンテナが、必ずマイクロサービスよりも先に起動する。
# pilot-agentの起動完了を待機する。
command:
- |
pilot-agent wait
# istio-proxyコンテナ終了直前の処理
preStop:
exec:
# istio-proxyコンテナが、必ずマイクロサービスよりも後に終了する。
# envoyプロセスとpilot-agentプロセスの終了を待機する。
command:
- "/bin/bash"
- "-c"
- |
sleep 5
while [ $(netstat -plnt | grep tcp | egrep -v 'envoy|pilot-agent' | wc -l) -ne 0 ]; do sleep 1; done
# マイクロサービスとistio-proxyコンテナの両方が終了するのを待つ
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 45
05. Gateway¶
.spec.selector¶
▼ selectorとは¶
Istio Ingress Gateway/EgressGatewayに付与された .metadata.labels キーを設定する。
デフォルトでは、Istio Ingress Gatewayには istio ラベルがあり、値は ingressgateway である。
また、Istio Egress Gatewayには istio ラベルがあり、値は egressgateway である。
*実装例*
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: foo-ingress
spec:
selector:
istio: istio-ingressgateway
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: istio-ingressgateway
istio: ingressgateway
.spec.servers.port¶
▼ name¶
Istio Ingress Gateway/EgressGatewayのPodで待ち受けるポート名を設定する。
*実装例*
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: foo-ingress
spec:
servers:
- port:
name: http
▼ number¶
Istio Ingress Gateway/EgressGatewayのPodで待ち受けるポート番号を設定する。
Ingress Nginx Controllerであれば、Nginx Controller Podで待ち受けるコンテナポート番号に相当する。
IngressGatewayの内部的なServiceのタイプに関して、NodePort Serviceを選んだ場合、Nodeの宛先ポート番号に合わせる。
一方で、LoadBalancer Serviceを選んだ場合、LoadBalancerがルーティングできる宛先ポート番号とする。
*実装例*
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: foo-ingress
spec:
servers:
- port:
number: 30000
▼ protocol¶
Istio Ingress Gateway/EgressGatewayのPodで受信するプロトコルを設定する。
ドキュメントは更新されていないが、執筆時点 (2025/03/10) で以下のプロトコルに対応している。
- TCP
- UDP
- gRPC
- gRPC-Web
- HTTP
- HTTP_PROXY
- HTTP2
- HTTPS
- TLS
- Mongo
- Redis
- MySQL
*実装例*
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: foo-ingress
spec:
servers:
- port:
protocol: HTTP
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: foo-egress
spec:
servers:
- port:
protocol: MySQL
▼ targetPort¶
Istio Ingress Gateway/EgressGatewayのPodの宛先ポート番号を設定する。
*実装例*
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: foo-ingress
spec:
servers:
- port:
targetPort: 80
.spec.servers.hosts¶
Gatewayでフィルタリングするインバウンド通信の Host ヘッダー名を設定する。
Istio Ingress Gatewayでは、複数のマイクロサービスでAPIを公開している場合、ワイルドカード (*) を使用して全てのドメインを許可することになる。
また、Istio Egress Gatewayでも任意のAPIへの接続を許可するために、同様にワイルドカード (*) を使用することになる。
*実装例*
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: foo-ingress
spec:
servers:
- hosts:
- "*"
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: bar-egress
spec:
servers:
- hosts:
- "*"
.spec.servers.tls.caCertificates¶
.spec.servers.tls.mode キーで相互TLS認証を設定している場合、クライアント証明書のペアになるCA証明書が必要である。
*実装例*
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: foo-ingress
spec:
servers:
- tls:
caCertificates: root-cert.pem
.spec.servers.tls.credentialName¶
CAを含むサーバー証明書を保持するSecretを設定する。
サーバー証明書のファイルを指定する場合は、.spec.servers[*].tls.serverCertificate キーを設定する。
Secretを更新した場合、Podを再起動せずに、PodにSecretを再マウントできる。
*実装例*
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: foo-ingress
spec:
servers:
- tls:
credentialName: istio-gateway-certificate-secret
.spec.servers.tls.mode¶
▼ modeとは¶
送信元とGatewayの間の暗号化方式を設定する。
▼ SIMPLE¶
送信元とGatewayの通信間で通常のHTTPSを実施する。
クライアント証明書は不要にである。
*実装例*
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: foo-ingress
spec:
servers:
- tls:
mode: SIMPLE
▼ MUTUAL¶
送信元とGatewayの間で、Istioの作成していない証明書による相互TLS認証を実施する。
*実装例*
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: foo-ingress
spec:
servers:
- tls:
mode: MUTUAL
▼ ISTIO_MUTUAL¶
送信元とGatewayの間で、Istioの作成した証明書による相互TLS認証を実施する。
istio-proxyとIstio Egress Gatewayの間で相互TLS認証を実施する場合、これを使用する。
*実装例*
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: foo-ingress
spec:
servers:
- tls:
mode: ISTIO_MUTUAL
▼ PASSTHROUGH¶
GatewayでHTTPSリクエストを受信した場合、サーバー証明書を検証をせずに、HTTPSをそのまま通過させる。
つまり、Gatewayの宛先にサーバー証明書を設定する必要がある。
PASSTHROUGH 以外のモードでは、GatewayでSSLを検証し、場合にとってはSSL終端となる。
注意点として、Gatewayは受信したHTTPSをTCPプロトコルとして処理するため、L7 ヘッダーにあるHTTPヘッダーやパスを使用してトラフィックを制御できない。
*実装例*
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: foo-ingress
spec:
servers:
- tls:
mode: PASSTHROUGH
- https://cloud.google.com/service-mesh/docs/security/egress-gateway-gke-tutorial?hl=ja#pass-through_of_httpstls_connections
- https://www.danielstechblog.io/run-the-istio-ingress-gateway-with-tls-termination-and-tls-passthrough/amp/
- https://istio.io/latest/docs/tasks/traffic-management/ingress/ingress-sni-passthrough/#configure-an-ingress-gateway
.spec.servers.tls.privateKey¶
*実装例*
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: foo-ingress
spec:
servers:
- tls:
privateKey: /etc/certs/privatekey.pem
.spec.servers.tls.serverCertificate¶
サーバー証明書のファイルを設定する。
.spec.servers.tls.mode キーで相互TLS認証を設定している場合、クライアント証明書のペアになるサーバー証明書が必要である。
サーバー証明書を保持するSecretを指定する場合は、.spec.servers[*].tls.credentialName キーを設定する。
*実装例*
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: foo-ingress
metadata:
name: gateway
spec:
servers:
- tls:
serverCertificate: /etc/certs/server.pem
06. PeerAuthentication¶
.spec.selector¶
指定したNamespaceの特定のPodで相互TLS認証を有効化する
*実装例*
apiVersion: security.istio.io/v1
kind: PeerAuthentication
metadata:
# foo内の全てのistio-proxyにPeerAuthenticationを適用する
namespace: foo
name: peer-authentication
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: foo
mtls:
mode: STRICT # 相互TLS認証を使用する。
.spec.mtls¶
▼ mtls¶
特定のNamespace内のすべてのistio-proxy間通信時、相互TLS認証を有効化するか否かを設定する。
特定のPod間でのみ相互TLS認証を使用したい場合、DestinationRuleでサーバー証明書を設定する。
▼ mode¶
相互TLS認証のタイプを設定する。
| 項目 | 説明 |
|---|---|
UNSET |
記入中... |
DISABLE |
相互TLS認証を使用しない。 |
PERMISSIVE |
相互TLS認証の時、istio-proxyは受信するプロトコルでHTTPSプロトコルとHTTPプロトコルの両方を許可する。 |
STRICT |
相互TLS認証の時、istio-proxyは受信するプロトコルでHTTPSプロトコルのみを許可し、HTTPを許可しない。 |
*実装例*
apiVersion: security.istio.io/v1
kind: PeerAuthentication
metadata:
# foo内の全てのistio-proxyにPeerAuthenticationを適用する
namespace: foo
name: peer-authentication
spec:
mtls:
mode: STRICT # 相互TLS認証を使用する。
相互TLS認証を使用する場合はサーバー証明書が必要になり、サーバー証明書が無いと以下のようなエラーになってしまう。
transport failure reason: TLS error: *****:SSL routines:OPENSSL_internal:SSLV3_ALERT_CERTIFICATE_EXPIRED
07. ProxyConfig¶
concurrency¶
サービスメッシュ全体、特定Namespace、特定ワークロードのistio-proxyにて、ワーカースレッド数を設定する。
.meshConfig.defaultConfig キーにデフォルト値を設定しておき、ProxyConfigでNamespaceやマイクロサービスPodごとに上書きするのがよい。
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1beta1
kind: ProxyConfig
metadata:
name: foo-proxyconfig
spec:
concurrency: 0
environmentVariables¶
サービスメッシュ全体、特定Namespace、特定ワークロードのistio-proxyにて、環境変数を設定する。
.meshConfig.defaultConfig キーにデフォルト値を設定しておき、ProxyConfigでNamespaceやマイクロサービスPodごとに上書きするのがよい。
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1beta1
kind: ProxyConfig
metadata:
name: foo-proxyconfig
spec:
environmentVariables:
# 値をダブルクオートで囲う
ISTIO_META_DNS_CAPTURE: "false"
08. RequestAuthentication¶
.metadata.namespace¶
RequestAuthenticationの適用範囲の仕組みは、AuthorizationPolicyと同じである。
作成したNamespaceに対して適用され、istio-system に置いた場合は全てのNamespaceに適用される。
もし、適用範囲を小さくしたい場合は、.spec.selector キーを使用する。
IstioコントロールプレーンのログからRequestAuthenticationをデバッグできる。
$ kubectl logs <IstiodコントロールプレーンのPod> -n istio-system
.spec.jwtRules¶
▼ jwtRulesとは¶
Bearer認証で使用するJWTトークンの発行元IDプロバイダーを設定する。
JWTトークンが失効していたり、不正な場合、認証処理を失敗として 401 レスポンスを返信する。
注意点として、そもそもリクエストにJWTが含まれていない場合には認証処理をスキップできてしまう。
代わりに、JWTが含まれていないリクエストをAuthorizationPolicyによる認可処理失敗 (403 ステータス) として扱う必要がある。
apiVersion: security.istio.io/v1
kind: RequestAuthentication
metadata:
name: foo-request-authentication-jwt
spec:
jwtRules:
# JWTトークンの発行元IDプロバイダーの識別子を設定する
# ブラウザから接続する
- issuer: https://foo-issuer.com
# IDプロバイダーのJWKsエンドポイントを設定し、アクセストークン署名検証のための公開鍵を取得する
# ブラウザから、またはAPIに直接接続する
jwksUri: https://example.com/.well-known/jwks.json
# 既存のJWTを再利用し、宛先マイクロサービスにそのまま転送する
forwardOriginalToken: true
# Authorizationヘッダーを指定する
fromHeaders:
- name: Authorization
prefix: "Bearer "
---
# RequestAuthenticationで設定したAuthorizationヘッダーがない場合には認可エラーとする
apiVersion: security.istio.io/v1
kind: AuthorizationPolicy
metadata:
name: foo-authorization-policy
spec:
# 許可する
action: ALLOW
rules:
- when:
- key: request.auth.claims[iss]
# JWTトークンがある場合にのみ許可する
values: ["foo-issuer.com"]
▼ issuer¶
JWTトークンの発行元IDプロバイダーの識別子を設定する。
JWTトークンの発行元IDプロバイダーの情報を取得できる。
ブラウザから接続する必要がある。
apiVersion: security.istio.io/v1
kind: RequestAuthentication
metadata:
name: foo-request-authentication-jwt
spec:
jwtRules:
- issuer: https://foo-issuer.com
▼ jwksUri¶
IDプロバイダーのJWKsエンドポイントを設定し、アクセストークン署名検証のための公開鍵を取得する
apiVersion: security.istio.io/v1
kind: RequestAuthentication
metadata:
name: foo-request-authentication-jwt
spec:
jwtRules:
- jwksUri: https://example.com/.well-known/jwks.json
▼ forwardOriginalToken¶
既存のJWTを再利用し、宛先マイクロサービスにそのまま伝播するフラグを設定する。
apiVersion: security.istio.io/v1
kind: RequestAuthentication
metadata:
name: foo-request-authentication-jwt
spec:
jwtRules:
- forwardOriginalToken: true
外部API (例:Google APIs) によっては、不要なJWTがリクエストヘッダーにあると、401 レスポンスを返信する。
そのため、外部APIに接続するマイクロサービスのRequestAuthenticationでは、forwardOriginalToken を false とし、JWTを削除しておく。
apiVersion: security.istio.io/v1
kind: RequestAuthentication
metadata:
name: foo-request-authentication-jwt
spec:
jwtRules:
- forwardOriginalToken: false
▼ fromCookies¶
Cookie ヘッダーの指定したキー名からアクセストークンを取得する。
Cookie ヘッダーを使用して認証アーティファクトを運搬する場合 (例:フロントエンドアプリケーションがCSRやSSR) に役立つ。
大文字 (.spec.jwtRules.fromCookies キー) ではないことに注意する。
apiVersion: security.istio.io/v1
kind: RequestAuthentication
metadata:
name: foo-request-authentication-jwt
spec:
jwtRules:
fromCookies:
# Cookieヘッダーの中でアクセストークンが設定されたキーを指定する
- <アクセストークンキー>
▼ fromHeaders¶
指定したヘッダーからアクセストークンを取得する。
Authorization ヘッダーを使用して認証アーティファクトを運搬する場合 (例:フロントエンドアプリケーションがCSR) に役立つ。
apiVersion: security.istio.io/v1
kind: RequestAuthentication
metadata:
name: foo-request-authentication-jwt
spec:
jwtRules:
fromHeaders:
# Authorizationヘッダーを指定する
- name: Authorization
prefix: "Bearer "
▼ outputPayloadToHeader¶
JWTを伝播するための新しいヘッダー名を設定する。
検証後のJWTを新しいヘッダーに割り当て、宛先マイクロサービスに伝播する。
apiVersion: security.istio.io/v1
kind: RequestAuthentication
metadata:
name: foo-request-authentication-jwt
spec:
jwtRules:
- outputPayloadToHeader: X-Authorization
.spec.selector¶
JWTによるBearer認証を適用するKubernetesリソース名を設定する。
apiVersion: security.istio.io/v1
kind: RequestAuthentication
metadata:
name: foo-request-authentication-jwt"
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: istio-ingressgateway
09. ServiceEntry¶
.spec.addresses¶
ルーティング先のIPアドレスを設定する。
L4 プロトコル (TCPLなど) では、リクエストにHostヘッダーがない。
これらのプロトコルでは、.spec.hosts キーの値を無視し、IPアドレスにリクエストをルーティングする。
なお、.spec.hosts キーは必須であり省略できないため、便宜上ではあるが何らかの名前をつけておく。
送信側のVirtualServiceの destination では、Hostヘッダーに "." をつけないとエラーになるため、受信側のServiceEntryも合わせておく (例:tcp.smtp) とよい。
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: ServiceEntry
metadata:
name: foo-mysql
spec:
exportTo:
- "*"
hosts:
# L4プロトコルでは、この設定は実際には使われない
# VirtualServiceでは "." をつけないとエラーになるため、ServiceEntryも合わせておく
- tcp
address:
# L4プロトコルでは、この設定でルーティングする
- 127.0.0.1/32
location: MESH_EXTERNAL
ports:
- number: 587
name: tcp
protocol: TCP
L7 プロトコル (HTTP、HTTPS、MySQLなど) では、リクエストにHostヘッダーがある。
送信側のVirtualServiceの .spec.http[*].route[*].destination では、Hostヘッダーに "." をつけないとエラーになるため、受信側のServiceEntryも合わせておく (例:tcp.smtp) とよい。
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: ServiceEntry
metadata:
name: foo-mysql
spec:
exportTo:
- "*"
hosts:
- <DBクラスター名>.cluster-<id>.ap-northeast-1.rds.amazonaws.com
location: MESH_EXTERNAL
ports:
- number: 3306
name: tcp-mysql
protocol: TCP
# Hostヘッダーがあるため、DNSでIPアドレスを取得する
resolution: DNS
.spec.exportTo¶
▼ exportToとは¶
そのServiceEntryにリクエストできるNamespaceを設定する。
ServiceEntryはIstio Egress Gatewayからリクエストを受信するため、基本的には * となるはずである。
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: ServiceEntry
metadata:
name: foo-service-entry
spec:
exportTo:
- "*"
.spec.hosts¶
▼ hostsとは¶
コンフィグストレージに登録する宛先のドメイン名を設定する。
部分的にワイルドカード (*) を使用できるが、全てのドメインを許可 (ワイルドカードのみ) できない。
*実装例*
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: ServiceEntry
metadata:
name: foo-service-entry
spec:
hosts:
- foo.com
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: ServiceEntry
metadata:
name: mysql-service-entry
spec:
hosts:
- <DBクラスター名>.cluster-<id>.ap-northeast-1.rds.amazonaws.com
.spec.location¶
▼ locationとは¶
登録したシステムがサービスメッシュ内か否かを設定する。
▼ MESH_EXTERNAL¶
登録したシステムがサービスメッシュ外にあることを表す。
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: ServiceEntry
metadata:
name: foo-service-entry
spec:
location: MESH_EXTERNAL
▼ MESH_INTERNAL¶
登録したシステムがサービスメッシュ内にあることを表す。
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: ServiceEntry
metadata:
name: foo-service-entry
spec:
location: MESH_INTERNAL
.spec.ports¶
▼ portsとは¶
コンフィグストレージに登録する宛先のポート番号を設定する。
*実装例*
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: ServiceEntry
metadata:
name: foo-service-entry
spec:
ports:
- name: tcp-mysql
number: 3306
protocol: TCP
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: ServiceEntry
metadata:
name: foo-service-entry
spec:
ports:
- name: http
number: 80
protocol: HTTP
- name: https
number: 443
protocol: HTTPS
.spec.resolution¶
▼ resolutionとは¶
コンフィグストレージに登録する宛先のIPアドレスの設定する。
▼ DNS¶
DNSサーバーから返信されたIPアドレスを許可する。
サービスメッシュ外のパブリックなドメインに接続する場合は、必須である。
*実装例*
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: ServiceEntry
metadata:
name: foo-service-entry
spec:
resolution: DNS
▼ NONE¶
Istio Egress Gatewayは値に注意が必要である。
ServiceEntryに対するリクエストの宛先IPアドレスはIstio Egress Gatewayに書き換えられている。
そのため、DNS解決を NONE にすると、Istio Egress GatewayはServiceEntryを見つけられず、自分自身でループしてしまう。
*実装例*
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: ServiceEntry
metadata:
name: foo-service-entry
spec:
resolution: DNS
10. Sidecar¶
.spec.workloadSelector¶
適用対象のWorkloadを設定する。
設定しない場合、Namespace内の全てのPodが対象になる。
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: Sidecar
metadata:
name: foo
namespace: foo
spec:
workloadSelector:
labels:
app: foo-1
.spec.ingress¶
インバウンド通信のプロキシ時の接続情報を設定する。
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: Sidecar
metadata:
name: foo
namespace: foo
spec:
workloadSelector:
labels:
app: foo-1
ingress:
- port:
number: 80
protocol: HTTP
name: http-ingress
defaultEndpoint: 127.0.0.1:80
.spec.egress¶
アウトバウンド通信のプロキシ時の接続情報を設定する。
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: Sidecar
metadata:
name: foo
namespace: foo
spec:
workloadSelector:
labels:
app: foo-1
egress:
- port:
number: 80
protocol: HTTP
name: http-egress
hosts:
- bar-namespace.svc.cluster.local
11. Telemetry¶
.metadata.namespace¶
NamespaceでTelemetyの対象のistio-proxyを絞れる。
もし istio-system を指定した場合、Root Namespaceという設定になり、istio-proxyコンテナのある全てのNamespaceが対象になる。
apiVersion: telemetry.istio.io/v1
kind: Telemetry
metadata:
# もしistio-systemを指定した場合は、istio-proxyコンテナのある全てのNamespaceが対象になる
namespace: foo
accessLogging¶
▼ accessLoggingとは¶
同じNamespace内のistio-proxyを対象として、アクセスログの作成方法を設定する。
apiVersion: telemetry.istio.io/v1
kind: Telemetry
metadata:
name: access-log-provider
# istio-proxyをインジェクションしている各Namespaceで作成する
# もしistio-systemを指定した場合は、istio-proxyコンテナのある全てのNamespaceが対象になる
namespace: foo
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
name: app
# Envoyをアクセスログプロバイダーとして設定する
accessLogging:
- providers:
- name: envoy
ConfigMapで設定する場合は、以下のように設定する。
Telemetryによる設定が推奨である。
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: istio-mesh-cm
namespace: istio-system
data:
mesh: |
accessLogFile: /dev/stdout
metrics¶
▼ metricsとは¶
同じNamespace内のistio-proxyを対象として、メトリクスの作成方法を設定する。
apiVersion: telemetry.istio.io/v1
kind: Telemetry
metadata:
name: metrics-provider
# istio-proxyをインジェクションしている各Namespaceで作成する
# もしistio-systemを指定した場合は、istio-proxyコンテナのある全てのNamespaceが対象になる
namespace: foo
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
name: app
metrics:
- providers:
- name: prometheus
tracing¶
▼ tracingとは¶
同じNamespace内のistio-proxyを対象として、スパンの作成方法を設定する。
apiVersion: telemetry.istio.io/v1
kind: Telemetry
metadata:
name: trace-provider
# istio-proxyをインジェクションしている各Namespaceで作成する
# もしistio-systemを指定した場合は、istio-proxyコンテナのある全てのNamespaceが対象になる
namespace: foo
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
name: app
tracing:
- providers:
- name: opentelemetry
randomSamplingPercentage: 100
▼ customTags¶
スパン属性を設定する。
apiVersion: telemetry.istio.io/v1
kind: Telemetry
metadata:
name: trace-provider
namespace: foo
spec:
tracing:
- providers:
- name: opentelemetry
customTags:
# HTTPヘッダーから設定する
http.url.path:
header:
name: :path
defaultValue: unknown
# 独自の属性を設定する
system.name:
literal:
value: foo
# 独自の属性を設定する
system.environment:
literal:
value: dev
12. VirtualService¶
.spec.exportTo¶
▼ exportToとは¶
そのVirtualServiceにリクエストできるNamespaceを設定する。
▼ * (アスタリスク)¶
デフォルト値である。
他のNamespaceのGatewayやDestinationRuleに紐づける場合、* とする必要がある。
もし、同じNamespace内のGatewayやDestinationRuleと紐づける場合、. とする。
つまり、Istio Ingress GatewayやIstio Egress Gatewayとリクエストを送受信するVirtualServiceとDestinationRuleでは * とし、それ以外のこれらの場合は . とする。
*実装例*
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: foo-virtual-service
spec:
exportTo:
- "*"
gateways:
- foo-igress
# Istio Ingress Gatewayは複数の種類のAPIへのリクエストを受信する
# そのため、後続のVirtualServiceでは、複数の種類のHostヘッダー値を受信するため、ワイルドカードとする
hosts:
- "*"
▼ . (ドット)¶
同じNamespace内のGatewayやDestinationRuleと紐づける場合、. とする。
もし、他のNamespaceのGatewayやDestinationRuleに紐づける場合、* とする必要がある。
つまり、Istio Ingress GatewayやIstio Egress Gatewayとリクエストを送受信するVirtualServiceとDestinationRuleでは * とし、それ以外のこれらの場合は . とする。
*実装例*
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: foo-virtual-service
spec:
exportTo:
- "."
gateways:
# デフォルト値のため、設定は不要である
- mesh
.spec.hosts¶
▼ hostsとは¶
VirtualServiceの設定値を適用する Host ヘッダー値を設定する。
ワイルドカード (*) を使用して全てのドメインを許可しても良いが、特定のマイクロサービスへのリクエストのみを扱うため、ホスト名もそれのみを許可すると良い。
なお、.spec.gateways キーで mesh (デフォルト値) を使用する場合、ワイルドカード以外を設定しないといけない。 (例:.spec.hosts キーを設定しない、特定のHostヘッダー値を設定するなど)
*実装例*
全てのHostヘッダー値でVirtualServiceを適用する。
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: foo-virtual-service
spec:
# 特定のマイクロサービスへのリクエストのみを扱うため、ホスト名もそれのみを許可する
# ただし、gatewaysオプションがあるVirtualServiceではワイルドカードする
hosts:
- foo
.spec.gateways¶
▼ gatewaysとは¶
インバウンド通信をいずれのGatewayから受信するかを設定する。
▼ <Namespace名>/<Gateway名>¶
いずれのGatewayの条件に合致したリクエストを処理するかを設定する。
Gateway名とこれのNamespaceを設定する。
VirtualServiceとGatewayが同じNamespaceに所属する場合は、Namespaceを省略できる (.spec.export キーとは関係ない) 。
ただ、Namespaceは省略しないほうがわかりやすい。
*実装例*
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: foo-virtual-service
spec:
gateways:
- foo-namespace/foo-gateway
# Istio Ingress Gatewayは複数の種類のAPIへのリクエストを受信する
# そのため、後続のVirtualServiceでは、複数の種類のHostヘッダー値を受信するため、ワイルドカードとする
hosts:
- "*"
▼ <Gateway名>¶
いずれのGatewayの条件に合致したリクエストを処理するかを設定する。
VirtualServiceを、Istio Ingress Gateway/EgressGatewayに紐づける場合 (サービスメッシュ内外の通信) は <Gateway名> とする。
VirtualServiceとGatewayが同じNamespaceに所属する場合は、Namespaceを省略できる (.spec.export キーとは関係ない) 。
ただ、Namespaceは省略しないほうがわかりやすい。
*実装例*
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: foo-ingress-virtual-service
spec:
gateways:
- foo-ingressgateway
# Istio Ingress Gatewayは複数の種類のAPIへのリクエストを受信する
# そのため、後続のVirtualServiceでは、複数の種類のHostヘッダー値を受信するため、ワイルドカードとする
hosts:
- "*"
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: foo-virtual-service-egress
spec:
hosts:
# Hostヘッダー値がexternal.comの時にVirtualServiceを適用する。
- external.com
gateways:
# PodからIstio Egress GatewayのPodへの通信で使用する
# gateway名と両方設定する場合は、デフォルト値としての省略はできない
- mesh
# Istio Egress Gatewayからエントリ済みシステムへの通信で使用する
- foo/foo-egressgateway
http:
# external.comに対するリクエストは、Istio Egress Gatewayにルーティング (リダイレクト) する
- match:
- gateways:
# PodからIstio Egress GatewayのPodへの通信で使用する
- mesh
port: 80
route:
- destination:
host: istio-egressgateway.istio-egress.svc.cluster.local
port:
number: 80
# Istio Egress Gatewayに対するリクエストは、エントリ済システムにルーティングする
- match:
- gateways:
# Istio Egress Gatewayからエントリ済みシステムへの通信で使用する
- foo/foo-egressgateway
port: 80
route:
- destination:
# ServiceEntryの.spec.hostsキーで指定しているホスト値を設定する
# ただし、ServiceEntryがホストに対して名前解決できていないと、そのホスト値を設定できない
host: external.com
port:
number: 80
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: foo-virtual-service-egress
spec:
hosts:
# Hostヘッダー値がexternal.comの時にVirtualServiceを適用する。
- external.com
gateways:
# PodからIstio Egress GatewayのPodへの通信で使用する
- mesh
# Istio Egress Gatewayからエントリ済みシステムへの通信で使用する
- foo/foo-egressgateway
tls:
# external.comに対するリクエストは、Istio Egress Gatewayにルーティング (リダイレクト) する
- match:
- gateways:
# PodからIstio Egress GatewayのPodへの通信で使用する
- mesh
port: 443
sniHosts:
- external.com
route:
- destination:
host: istio-egressgateway.istio-egress.svc.cluster.local
port:
number: 443
http:
# Istio Egress Gatewayに対するリクエストは、エントリ済システムにルーティングする
- match:
- gateways:
# Istio Egress Gatewayからエントリ済みシステムへの通信で使用する
- foo/foo-egressgateway
port: 443
route:
- destination:
# ServiceEntryの.spec.hostsキーで指定しているホスト値を設定する
# ただし、ServiceEntryがホストに対して名前解決できていないと、そのホスト値を設定できない
host: external.com
port:
number: 443
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: foo-virtual-service-egress
spec:
exportTo:
- "*"
hosts:
# アプリはDBのFQDNを指定する
# VirtualSErviceではこれを指定する
- <DBクラスター名>.cluster-<id>.ap-northeast-1.rds.amazonaws.com
gateways:
- mesh
- foo/foo-egressgateway
tcp:
- match:
- gateways:
- mesh
port: 3306
route:
- destination:
host: istio-egressgateway.istio-egress.svc.cluster.local
port:
number: 3306
- match:
- gateways:
- foo-egress
port: 3306
route:
- destination:
# ServiceEntryにそのままのHostヘッダーでフォワーディングする
host: <DBクラスター名>.cluster-<id>.ap-northeast-1.rds.amazonaws.com
port:
number: 3306
▼ mesh¶
VirtualServiceを、Pod間通信で使用する場合は mesh (デフォルト値) とする。
Hostヘッダーに * (ワイルドカード) を使用できず、特定のHostヘッダーのみを許可する必要がある。
*実装例*
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: foo-virtual-service
spec:
gateways:
# デフォルト値のため、設定は不要である
- mesh
hosts:
# ワイルドカードを指定できず、特定のHostヘッダーを許可する必要がある
- account-app
.spec.http¶
HTTP/1.1、HTTP/2 (例:gRPC、GraphQLなど) のプロトコルによる通信をDestinationRuleに紐づくPodへルーティングする。
.spec.tcp キーや .spec.tls キーとは異なり、マイクロサービスがHTTPプロトコルで通信を送受信し、istio-proxy間で相互TLS認証を実施する場合、これを使用する。
.spec.http.corsPolicy¶
▼ corsPolicyとは¶
ブラウザではデフォルトでCORSが有効になっており、正しいリクエストがCORSを突破できるように対処する必要がある。
多くの場合、バックエンドアプリケーションでCORSに対処することが多いが、istio-proxyで対処できる。
.spec.http.fault¶
▼ faultとは¶
発生させるフォールトインジェクションを設定する。
*実装例*
503 ステータスのエラーを 100%の確率で発生させる。
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: foo-virtual-service
spec:
http:
- fault:
- abort:
# 発生させるエラー
httpStatus: 503
# エラーを発生させる確率
percentage:
value: 100
*実装例*
10 秒のレスポンスの遅延を 100%の確率で発生させる。
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: foo-virtual-service
spec:
http:
- fault:
- delay:
# レスポンスの遅延時間
fixedDelay: 10s
# 遅延レスポンスを発生させる割合
percentage:
value: 100
.spec.http.match¶
▼ matchとは¶
受信した通信のうち、ルールを適用するもののメッセージ構造を設定する。
▼ <ヘッダー名>¶
ヘッダー名で合致条件を設定する。
*実装例*
受信した通信のうち、x-foo ヘッダーに bar が割り当てられたものだけにルールを適用する。
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: foo-virtual-service
spec:
http:
- match:
- headers:
x-foo:
exact: bar
*実装例*
ユーザーエージェントで振り分ける。
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: foo-virtual-service
spec:
# Istio Ingress Gatewayは複数の種類のAPIへのリクエストを受信する
# ただし、gatewaysオプションがあるVirtualServiceではワイルドカードする
hosts:
- foo
http:
- match:
- headers:
user-agent:
regex: <PCのユーザーエージェント>
route:
- destination:
host: pc
- match:
- headers:
user-agent:
regex: <スマホのユーザーエージェント>
route:
- destination:
host: sp
▼ gateways¶
.spec.gateways キーで設定した <Gateway名> と mesh (デフォルト値) のうちで、その合致条件に使用するほうを設定する。
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: foo-virtual-ingress
spec:
exportTo:
- "*"
hosts:
- httpbin.org
gateways:
- foo-ingressgateway
- mesh
http:
- match:
- gateways:
# PodからIstio Egress GatewayのPodへの通信で使用する
- mesh
port: 443
route:
- destination:
host: istio-egressgateway.istio-egress.svc.cluster.local
port:
number: 443
- match:
- gateways:
# Istio Egress Gatewayからエントリ済みシステムへの通信で使用する
- foo-ingressgateway
port: 443
route:
- destination:
# ServiceEntryの.spec.hostsキーで指定しているホスト値を設定する
# ただし、ServiceEntryがホストに対して名前解決できていないと、そのホスト値を設定できない
host: httpbin.org
port:
number: 443
▼ uri¶
ヘッダー名で合致条件を設定する。
*実装例*
受信した通信のうち、URLの接頭辞が /foo のものだけにルールを適用する。
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: foo-virtual-service
spec:
http:
- match:
- headers:
uri:
prefix: /foo
.spec.http.retries¶
▼ retriesとは¶
リトライ条件を設定する。
なお、TCP接続には spec.tcp[*].retries キーのような同様の設定は存在しない。
*実装例*
500系ステータスの場合、attempts の数だけリトライする。
各リトライで処理の結果が返却されるまでの処理タイムアウト時間を perTryTimeout で設定する。
初回リクエストのリトライを timeout で、失敗時のリトライの処理タイムアウト時間を retries.perTryTimeout で設定する。
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: VirtualService
spec:
hosts:
- foo-service.foo-namespace.svc.cluster.local
http:
- route:
- destination:
host: foo-service.foo-namespace.svc.cluster.local
# 処理タイムアウト
timeout: 10s
# 初回リクエストの失敗時のリトライ
retries:
# 最大のリトライ回数
# リトライ間隔は、初回リクエストやリトライの処理タイムアウト時間によって、自動的に決まる
attempts: 3
# リトライの処理タイムアウト時間
perTryTimeout: 10s
# Envoyのx-envoy-retry-onの値
retryOn: gateway-error
Gateway系ステータス (502、503、504) の場合、attempts の数だけリトライする。
初回リクエストのリトライを timeout で、失敗時のリトライの処理タイムアウト時間を retries.perTryTimeout で設定する。
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: VirtualService
spec:
hosts:
- foo-service.foo-namespace.svc.cluster.local
http:
- route:
- destination:
host: foo-service.foo-namespace.svc.cluster.local
# 処理リクエスト
timeout: 10s
# 初回リクエストの失敗時のリトライ
retries:
# 最大のリトライ回数
# リトライ間隔は、初回リクエストやリトライの処理タイムアウト時間によって、自動的に決まる
attempts: 3
# リトライの処理タイムアウト時間
perTryTimeout: 10s
# Envoyのx-envoy-retry-onの値
retryOn: gateway-error
▼ attempt¶
istio-proxyのリバースプロキシに失敗した場合の最大リトライ回数を設定する。
Serviceへのルーティングの失敗ではないことに注意する。
*実装例*
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: foo-virtual-service
spec:
http:
- retries:
attempts: 3
▼ retryOn¶
リトライ失敗の理由を設定する。
istio-proxyは、レスポンスの x-envoy-retry-on ヘッダーに割り当てるため、これの値を設定する。
*実装例*
デフォルトでは、リトライの条件は connect-failure,refused-stream,unavailable である。
EXCLUDE_UNSAFE_503_FROM_DEFAULT_RETRY 変数を true にすると、元はデフォルト値であった 503 を設定できる。
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: foo-virtual-service
spec:
http:
- retries:
retryOn: connect-failure,refused-stream,unavailable
.spec.http.route¶
▼ destination.host¶
受信した通信で宛先のServiceのドメイン名 (あるいはService名) を設定する。
*実装例*
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: VirtualService
spec:
# Istio Ingress Gatewayは複数の種類のAPIへのリクエストを受信する
# ただし、gatewaysオプションがあるVirtualServiceではワイルドカードする
hosts:
- foo-service.foo-namespace.svc.cluster.local
http:
- route:
- destination:
# Service名でも良い。
host: foo-service.foo-namespace.svc.cluster.local
▼ destination.port¶
受信する通信でルーティング先のポート番号を設定する。
*実装例*
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: foo-virtual-service
spec:
# Istio Ingress Gatewayは複数の種類のAPIへのリクエストを受信する
# ただし、gatewaysオプションがあるVirtualServiceではワイルドカードする
hosts:
- foo-service.foo-namespace.svc.cluster.local
http:
- route:
- destination:
host: foo-service.foo-namespace.svc.cluster.local
port:
number: 80
▼ destination.subset¶

VirtualServiceを起点としたPodのカナリアリリースで使用する。
紐付けたいDestinationRuleのサブセット名と同じ名前を設定する。
DestinationRuleで受信した通信を、DestinationRuleのサブセットに紐づくPodへルーティングする。
*実装例*
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: foo-virtual-service
spec:
# Istio Ingress Gatewayは複数の種類のAPIへのリクエストを受信する
# ただし、gatewaysオプションがあるVirtualServiceではワイルドカードする
hosts:
- foo-service.foo-namespace.svc.cluster.local
http:
- route:
- destination:
# Service名でも良い
host: foo-service.foo-namespace.svc.cluster.local
port:
number: 80
subset: v1 # 旧Pod
weight: 70
- destination:
# Service名でも良い
host: foo-service.foo-namespace.svc.cluster.local
port:
number: 80
subset: v2 # 新Pod
weight: 30
▼ weight¶
Serviceの重み付けルーティングの割合を設定する。
.spec.http[*].route[*].destination.subset キーの値は、DestinationRuleで設定した .spec.subsets[*].name キーに合わせる必要がある。
重み付けの偏りの割合によって、カナリアリリースやB/Gデプロイメントを実現できる。
*実装例*
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: foo-virtual-service
spec:
# Istio Ingress Gatewayは複数の種類のAPIへのリクエストを受信する
# ただし、gatewaysオプションがあるVirtualServiceではワイルドカードする
hosts:
- foo-service.foo-namespace.svc.cluster.local
http:
- route:
- destination:
# Service名でも良い
host: foo-service.foo-namespace.svc.cluster.local
port:
number: 80
subset: v1 # 旧Pod
weight: 70
- destination:
# Service名でも良い
host: foo-service.foo-namespace.svc.cluster.local
port:
number: 80
subset: v2 # 新Pod
weight: 30
.spec.http.timeout¶
▼ timeoutとは¶
istio-proxyの宛先にリクエストを送信してから返信があるまでの処理タイムアウト時間を設定する (DestinationRuleは接続タイムアウト) 。
0 秒の場合、処理タイムアウトは無制限になる。
これは、Envoyのルートの grpc_timeout_header_max と timeout の両方に適用される。
指定した時間以内に、istio-proxyの宛先からレスポンスがなければ、istio-proxyは処理タイムアウト時間を超過したものとして処理する。
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: foo-virtual-service
spec:
http:
- route:
- destination:
# Service名でも良い
host: foo-service.foo-namespace.svc.cluster.local
port:
number: 80
subset: v1 # 旧Pod
weight: 70
- destination:
# Service名でも良い
host: foo-service.foo-namespace.svc.cluster.local
port:
number: 80
subset: v2 # 新Pod
weight: 30
# 処理タイムアウト
timeout: 40s
- https://istio.io/latest/docs/tasks/traffic-management/request-timeouts/
- https://www.envoyproxy.io/docs/envoy/latest/api-v3/config/route/v3/route_components.proto
- https://qiita.com/Takagi_/items/129acd03e76fce5c295b#%E5%AE%9F%E9%9A%9B%E3%81%ABhttp%E3%83%AA%E3%82%AF%E3%82%A8%E3%82%B9%E3%83%88%E3%81%AE%E3%82%BF%E3%82%A4%E3%83%A0%E3%82%A2%E3%82%A6%E3%83%88%E8%A8%AD%E5%AE%9A%E3%82%84%E3%82%A2%E3%82%A4%E3%83%89%E3%83%AB%E3%81%A8%E3%81%AA%E3%81%A3%E3%81%9F%E3%82%B3%E3%83%8D%E3%82%AF%E3%82%B7%E3%83%A7%E3%83%B3%E3%82%92%E5%88%87%E6%96%AD%E3%81%95%E3%81%9B%E3%82%8B%E3%81%AB%E3%81%AF%E3%81%A9%E3%81%86%E3%81%99%E3%82%8B%E3%81%AE%E3%81%8B
.spec.tcp¶
▼ tcpとは¶
.spec.http キーや .spec.tls キーとは異なり、TCPプロトコルや独自プロトコル (例:MySQLなど) による通信をDestinationRuleに紐づくPodへルーティングする。
▼ match¶
*実装例*
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: foo-virtual-service
spec:
tcp:
- match:
- port: 9000
▼ route.destination.host¶
.spec.http キーと同じ機能である。
*実装例*
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: foo-virtual-service
spec:
# Istio Ingress Gatewayは複数の種類のAPIへのリクエストを受信する
# ただし、gatewaysオプションがあるVirtualServiceではワイルドカードする
hosts:
- foo-service.foo-namespace.svc.cluster.local
tcp:
- route:
- destination:
# Service名でも良い
# foo-service
host: foo-service.foo-namespace.svc.cluster.local
▼ route.destination.port¶
.spec.http キーと同じ機能である。
*実装例*
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: foo-virtual-service
spec:
# Istio Ingress Gatewayは複数の種類のAPIへのリクエストを受信する
# ただし、gatewaysオプションがあるVirtualServiceではワイルドカードする
hosts:
- foo-service.foo-namespace.svc.cluster.local
tcp:
- route:
- destination:
# Service名でも良い
# foo-service
host: foo-service.foo-namespace.svc.cluster.local
port:
number: 9000
▼ route.destination.subset¶
.spec.http キーと同じ機能である。
*実装例*
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: foo-virtual-service
spec:
tcp:
- route:
- destination:
# Service名でも良い
# foo-service
host: foo-service.foo-namespace.svc.cluster.local
port:
number: 9000
subset: v1 # 旧Pod
weight: 70
- destination:
# Service名でも良い
# foo-service
host: foo-service.foo-namespace.svc.cluster.local
port:
number: 9000
subset: v2 # 新Pod
weight: 30
.spec.tls¶
▼ tlsとは¶
.spec.http キーや .spec.tcp キーとは異なり、HTTPSプロトコルの通信をDestinationRuleに紐づくPodへルーティングする。
マイクロサービスがHTTPSプロトコルで通信を送受信し、istio-proxy間で相互TLS認証を実施する場合、これを使用する。
他に、マイクロサービスがHTTPSリクエストを送信し、Istio Egress Gatewayでこれをそのまま通過させる (PASSTHROUGH) 場合も必要になる。
▼ Istio Egress GatewayのVirtualServiceでの注意点¶
.spec.tls キーで送信する場合、Istio Egress Gatewayはアプリケーションデータを復号できないため、プロトコルをTCPとして扱う。
そのため、Istio Egress Gateway上を通過するTLSはIstioのメトリクスではTCPとして処理され、またIstio Egress Gatewayではスパンを作成できない。
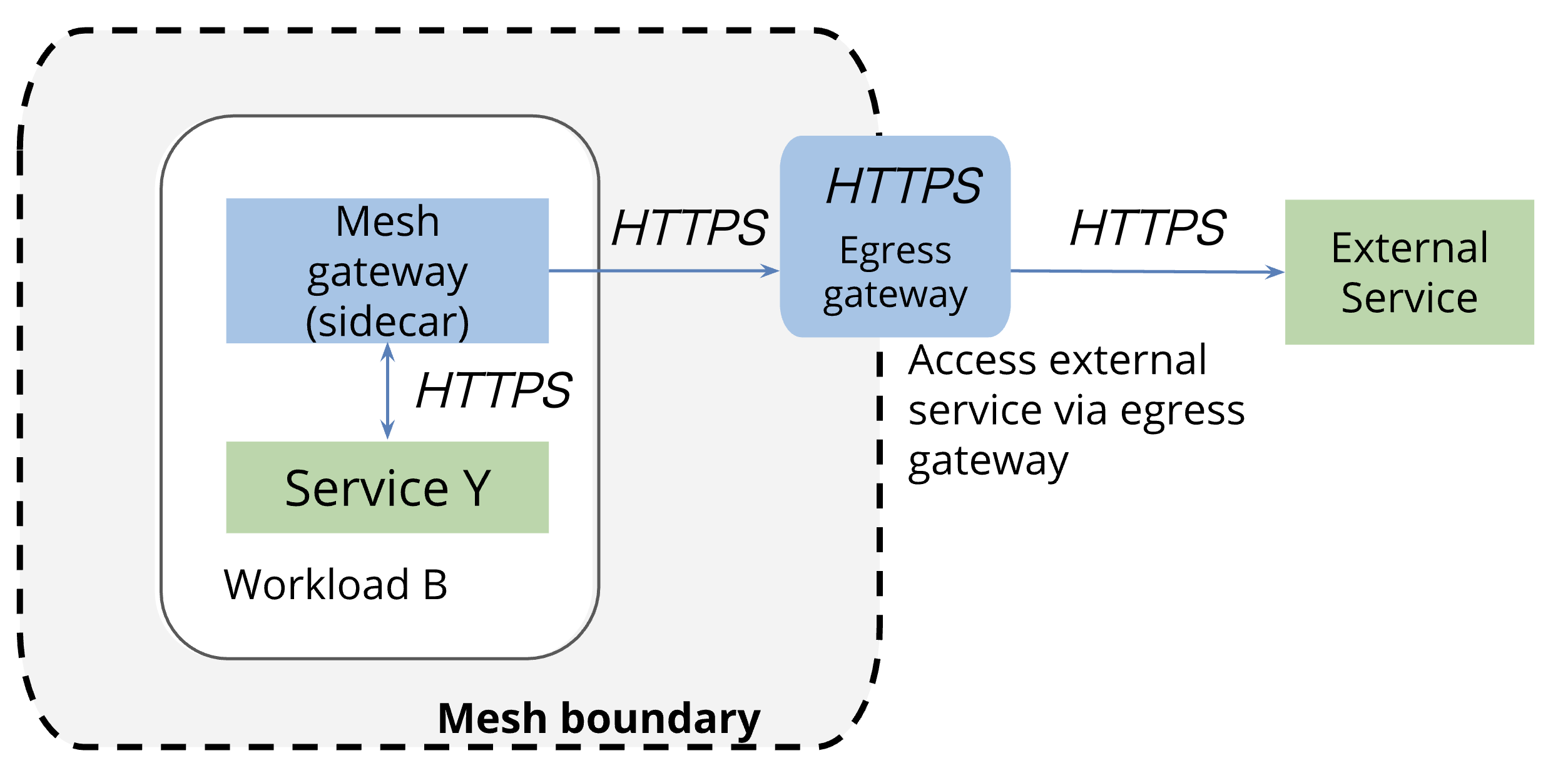
13. WorkloadEntry¶
Kubernetes Clusterの外にある単一の仮想サーバーをサービスメッシュ内で管理する。
DBをKubernetes Cluster外の仮想サーバー上で稼働させていたり、一部のマイクロサービスを仮想サーバー上で稼働させなければならない場合に役立つ。
ただし、仮想サーバー内でistioプロセスをインストールし、実行する必要がある。
# インストール
$ curl -LO https://storage.googleapis.com/istio-release/releases/1.24.2/deb/istio-sidecar.deb
$ sudo dpkg -i istio-sidecar.deb
... # 諸々の手順
# デーモンプロセスを実行
$ sudo systemctl start istio
14. WorkloadGroup¶
Kubernetes Clusterの外にある複数の仮想サーバーをサービスメッシュ内で管理する。
DBをKubernetes Cluster外の仮想サーバー上で稼働させていたり、一部のマイクロサービスを仮想サーバー上で稼働させなければならない場合に役立つ。
ただし、仮想サーバー内でistioプロセスをインストールし、実行する必要がある。
# インストール
$ curl -LO https://storage.googleapis.com/istio-release/releases/1.24.2/deb/istio-sidecar.deb
$ sudo dpkg -i istio-sidecar.deb
... # 諸々の手順
# デーモンプロセスを実行
$ sudo systemctl start istio