リソース@Istio¶
はじめに¶
本サイトにつきまして、以下をご認識のほど宜しくお願いいたします。
01. K8sリソース/IstioリソースとEnvoy設定値の関係¶
一覧表¶
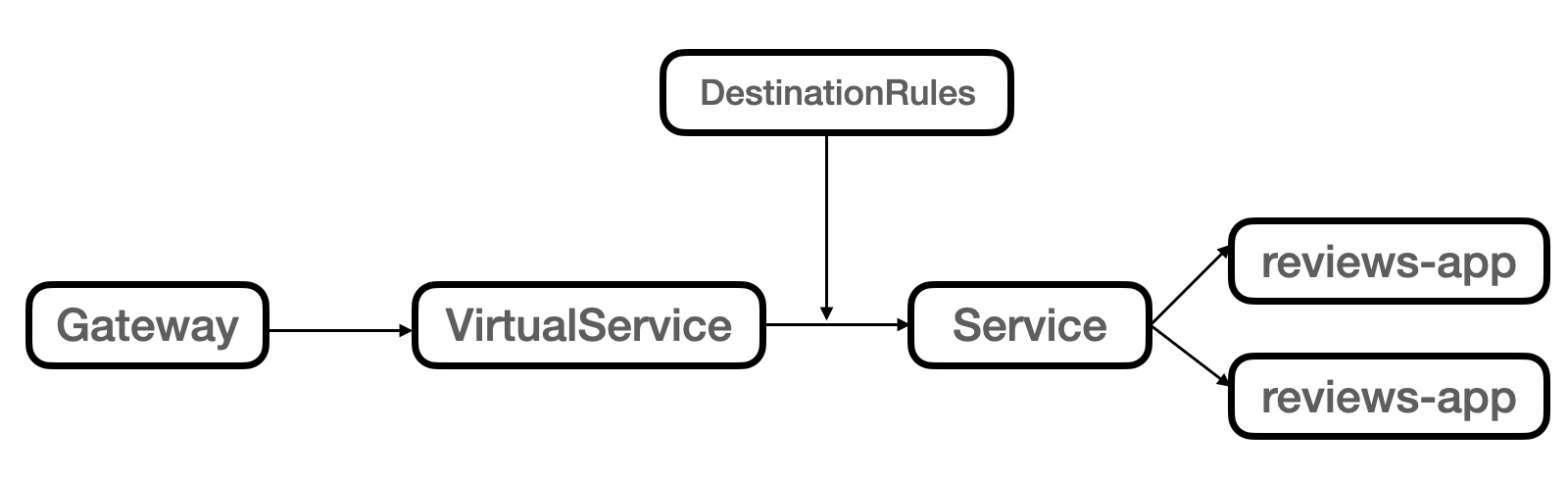
ルートへの変換¶
いずれのIstioリソースがルートに変換されたかは、ルートの metadata.filter_metadata キーで確認できる。
metadata:
filter_metadata:
istio:
config: /apis/networking.istio.io/v1alpha3/namespaces/foo-namespace/virtual-service/foo-virtual-service
クラスターへの変換¶
いずれのIstioリソースがクラスターに変換されたかは、クラスターの metadata.filter_metadata キーで確認できる。
metadata:
filter_metadata:
istio:
config: /apis/networking.istio.io/v1alpha3/namespaces/foo-namespace/destination-rule/foo-destination-rule
services:
- name: foo-service
host: foo-service.foo-namespace.svc.cluster.local
namespace: foo-namespace
02. Gateway¶
Gatewayとは¶
▼ ロードバランサーで使用する場合¶
Gatewayは、Istio Ingress Gatewayの一部として、Node外から受信した通信をフィルタリングする能力を担う。
▼ Pod間通信のみで使用する場合¶
Pod間通信には不要である。
Envoyの設定値として¶
▼ リスナーとして¶
Istiodコントロールプレーンは、Gatewayの設定値をEnvoyのリスナーに変換する。
なお、KubernetesのGatewayもEnvoyのリスナーと同等である。
$ kubectl exec \
-it foo-pod \
-n foo-namespace \
-c istio-proxy \
-- bash -c "curl http://127.0.0.1:15000/config_dump?resource={dynamic_listeners}" | yq -P
---
configs:
- "@type": type.googleapis.com/envoy.admin.v3.ListenersConfigDump.DynamicListener
# リスナー
name: 0.0.0.0_50002
active_state:
version_info: 2022-11-24T12:13:05Z/468
listener:
"@type": type.googleapis.com/envoy.config.listener.v3.Listener
name: 0.0.0.0_50002
address:
socket_address:
address: 0.0.0.0
port_value: 50002
# 使用するフィルターを設定する
filter_chains:
- filter_chain_match:
transport_protocol: raw_buffer
application_protocols:
- http/1.1
- h2c
filters:
- name: envoy.filters.network.http_connection_manager
typed_config:
# ネットワークフィルター (http_connection_manager) を指定する
"@type": type.googleapis.com/envoy.extensions.filters.network.http_connection_manager.v3.HttpConnectionManager
stat_prefix: outbound_0.0.0.0_50001
rds:
config_source:
ads: {}
initial_fetch_timeout: 0s
resource_api_version: V3
route_config_name: 50002
...
- "@type": type.googleapis.com/envoy.admin.v3.ListenersConfigDump.DynamicListener
...
02-02. Istio Ingress Gateway¶
Istio Ingress Gatewayとは¶
サービスメッシュ内宛の通信をロードバランシングする L4/L7 ロードバランサーを作成する。
GatewayとVirtualServiceの設定値に基づいて、Node外からインバウンド通信を受信し、Podにルーティングする。
KubernetesリソースのIngressの代わりとして使用できる。
Istio Ingress Gatewayの仕組み¶
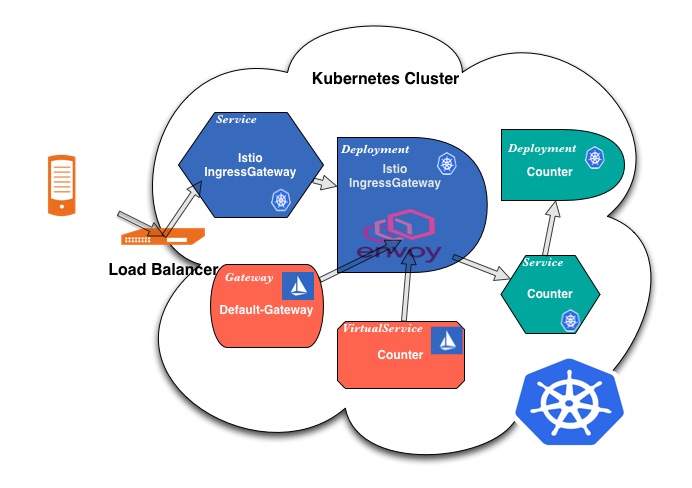
Istio Ingress Gatewayは、以下から構成される。
istio-ingressgatewayというService (NodePort ServiceまたはLoadBalancer Service)- Deployment配下の
istio-ingressgateway-*****というPod (istio-proxyのみが稼働)
Serviceは、おおよそGatewayの設定で決まる。
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
labels:
app: istio-ingressgateway
istio: ingressgateway
name: istio-ingressgateway
namespace: ingress
spec:
# Serviceタイプは選択可能である。
type: NodePort
# ルーティンング先のPod (istio-ingressgateway-*****) の識別子が設定される。
selector:
app: istio-ingressgateway
istio: ingressgateway
# ルーティング先のPodのポート番号が設定される。
ports:
- name: http-foo
# Nodeが待ち受けるポート番号
nodePort: 30001
# NodePort Serviceが待ち受けるポート番号
port: 443
protocol: TCP
# NodePort Serviceの宛先ポート番号 (Istio Ingress GatewayのPodが待ち受けるポート番号)
targetPort: 443
- name: http-bar
nodePort: 30002
port: 3000
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 3000
- name: http-baz
nodePort: 30003
port: 9090
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 9090
Podは、おおよそVirtualServiceの設定で決まる。
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
labels:
app: istio-ingressgateway
istio: ingressgateway
name: istio-ingressgateway
namespace: istio-ingress
spec:
containers:
- args:
# pilot-agent proxyコマンド
# https://istio.io/latest/docs/reference/commands/pilot-agent/#pilot-agent-proxy
- proxy
- router
- --domain
- $(POD_NAMESPACE).svc.cluster.local
- --proxyLogLevel=warning
- --proxyComponentLogLevel=misc:error
- --log_output_level=default:info
image: docker.io/istio/proxyv2:<リビジョン>
name: istio-proxy
# 待ち受けるポート番号の仕様
# コンテナの公開ポートがspec.containers[*].portsキーに定義されていなくても問題ない。
ports:
- containerPort: 15090
name: http-envoy-prom
protocol: TCP
...
# 重要なところ以外を省略しているため、全体像はその都度確認すること。
- https://software.danielwatrous.com/istio-ingress-vs-kubernetes-ingress/
- https://stackoverflow.com/questions/68711365/why-isnt-the-circuit-breaking-of-istio-working
- https://bcho.tistory.com/1367
- https://qiita.com/J_Shell/items/296cd00569b0c7692be7
- https://blog.jayway.com/2018/10/22/understanding-istio-ingress-gateway-in-kubernetes/
- https://layer5.io/learn/learning-paths/mastering-service-meshes-for-developers/introduction-to-service-meshes/istio/expose-services/
複数のIstio Ingress Gateway¶
もし複数のIstio Ingress Gateway DeploymentをHelmでデプロイする場合は、Istio Ingress Gatewayごとに、gatewayチャートのリリースを分けることになる。
チャートのアップグレードの作業が増えるが、責務 (パブリック/プライベート、宛先) を切り分けるユースケースがあってもよい。
- https://alibaba-cloud.medium.com/traffic-management-with-istio-1-unified-management-of-tcp-ingress-traffic-routing-based-on-909d961a3893
- https://medium.com/@dinup24/expose-apps-on-private-network-through-istio-ingress-gateway-7dcb8a16d5bc
- https://discuss.istio.io/t/how-to-run-multiple-ingress-gateway-with-different-class-names/1866
- https://getistio.io/istio-in-practice/multiple-ingress-gateways/
- https://istio.io/v1.13/blog/2018/v1alpha3-routing/
エラー¶
▼ 宛先Podに接続できない¶
upstream connect error or disconnect/reset before headers. reset reason: connection termination というエラーになる。
以下の場合がある。
- Istio Ingress Gatewayに関するService、VirtualService、JWTトークンleの設定の不備で接続できない
- タイムアウト時間が短すぎる
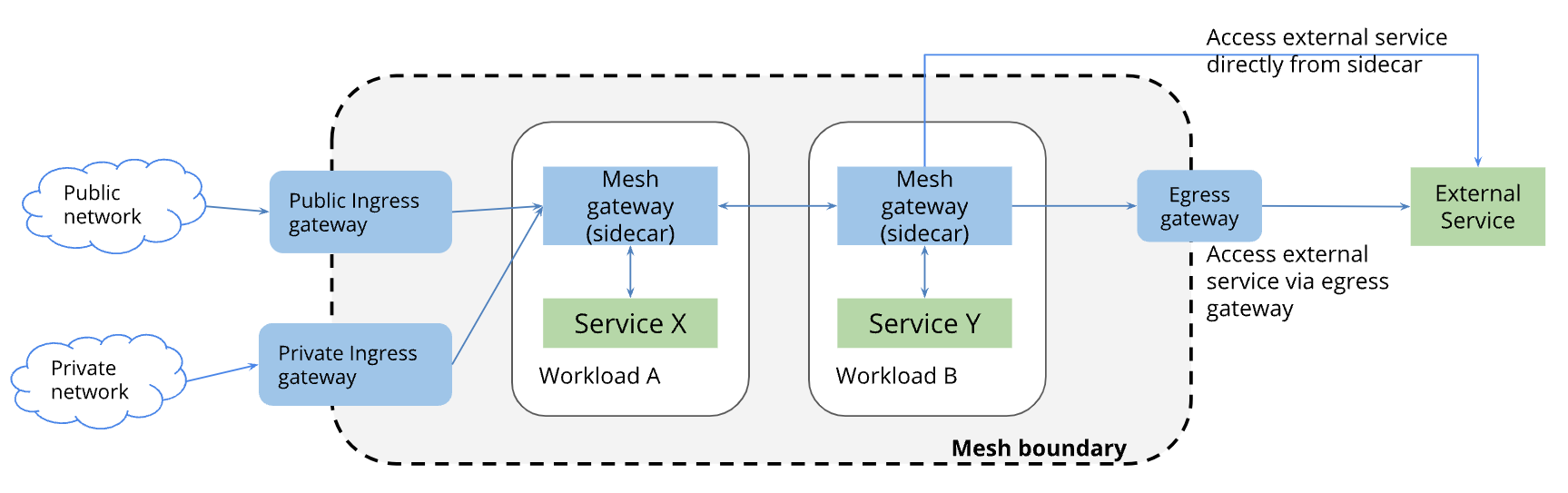
02-03. Istio Egress Gateway¶
Istio Egress Gatewayとは¶
Istio Egress Gatewayは、サービスメッシュ外宛ての通信をロードバランシングする L4/L7 ロードバランサーを作成する。
Clusterネットワーク内から通信を受信し、フィルタリングした後、Cluster外 (例:外部マイクロサービス、外部サービスのAPI、データベース、メッセージキューなど) にルーティングする。
Istio Egress Gatewayを使用しない場合、サービスメッシュ外への通信を監視できるようになり、またサイドカーを通過せずにサービスメッシュ外へ通信できてしまう。
しかし、Istio Egress Gatewayを使わないと、マイクロサービスからistio-proxyコンテナを経由せず、外部システムに直接HTTPSリクエストを送信できるようになってしまう。このため、システムの安全性が低くなる。
他に、サービスメッシュ外への特定の通信を識別できるようになるメリットもある。
Envoyの設定値として¶
Istiodコントロールプレーンは、ServiceEntryの設定値をEnvoyのクラスターに変換する。
送信元PodとIstio Egress Gateway間の通信¶
▼ 相互TLS認証¶
送信元マイクロサービスはHTTPを指定し、istio-proxyのクライアント証明書とIstio Egress Gatewayのサーバー証明書で相互TLS認証を実施する。
Istio Egress Gatewayはアプリケーションデータを復号できるため、プロトコルをHTTPとして扱う。
そのため、IstioのメトリクスではHTTPとして処理され、またIstio Egress Gatewayではスパンを作成できる。
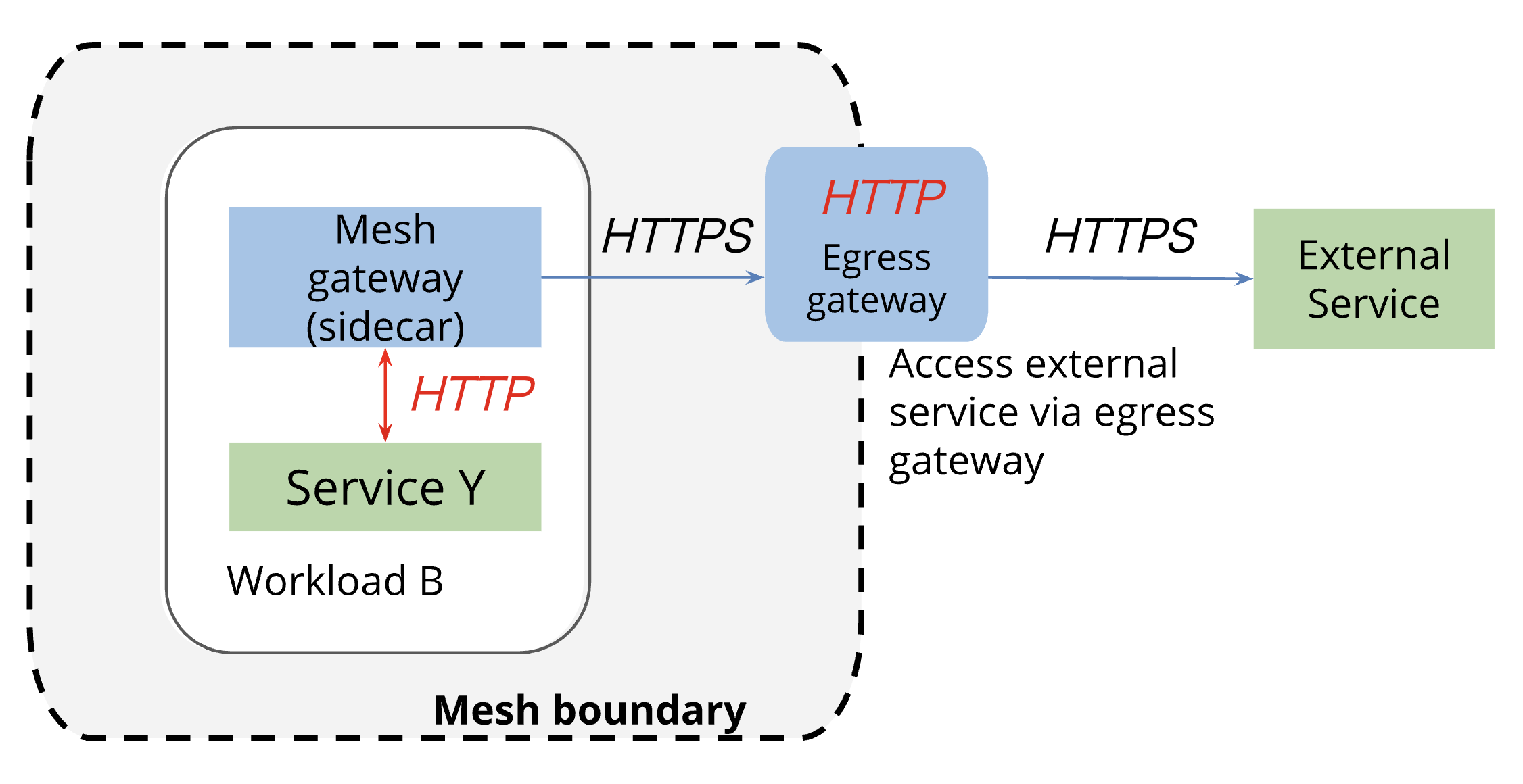
▼ サーバー認証 (Passthrough)¶
送信元マイクロサービスはHTTPSを指定し、サービスメッシュ外の宛先が持つサーバー証明書でサーバー認証を実施する。
Istio Egress Gatewayはアプリケーションデータを復号できないため、プロトコルをTCPとして扱う。
そのため、Istio Egress Gateway上を通過するTLSはIstioのメトリクスではTCPとして処理され、またIstio Egress Gatewayではスパンを作成できない。
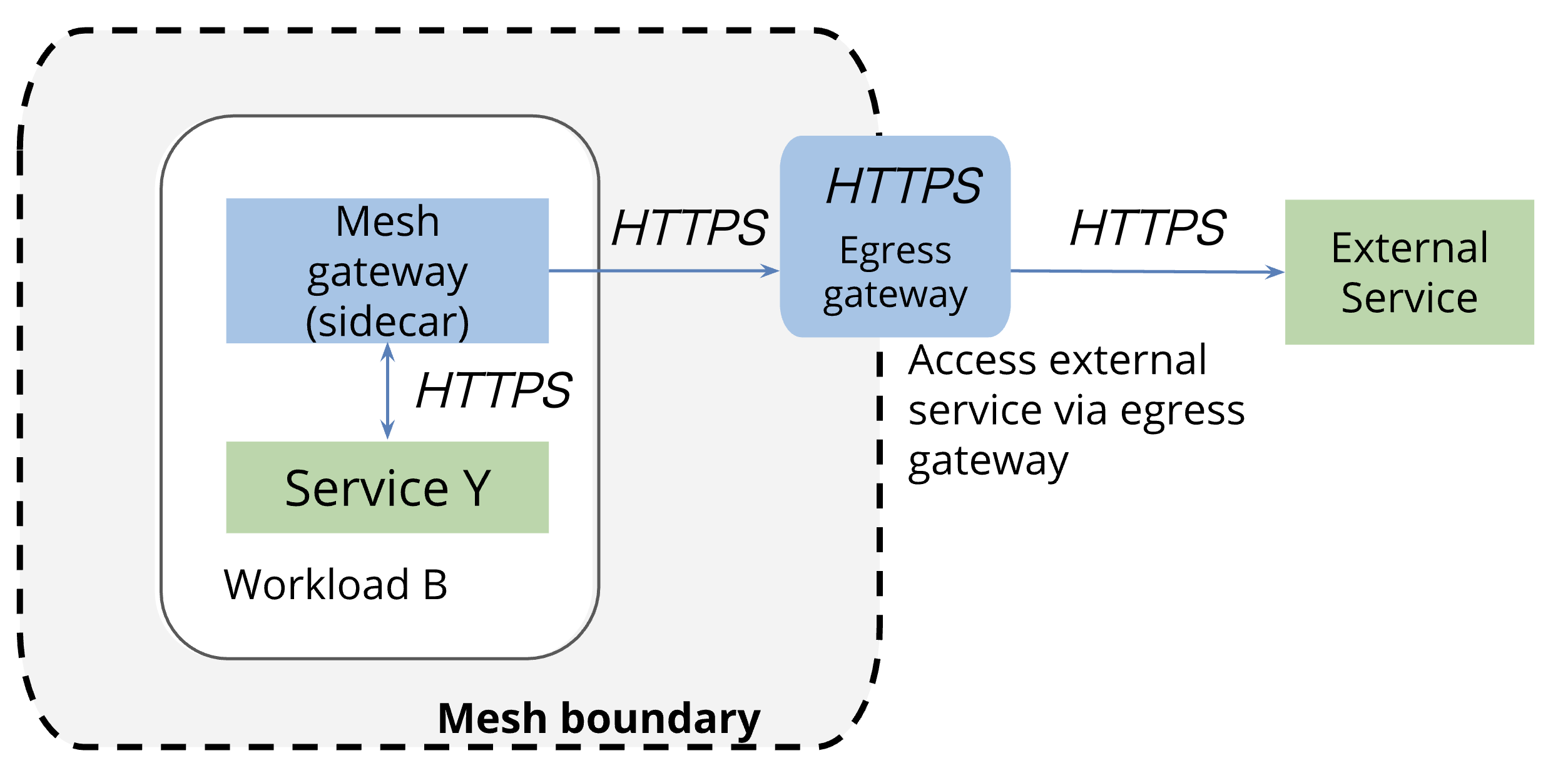
関連するIstioリソース¶
Istioサイドカーモードとアンビエントモードの間で、Istio Egress Gatewayに必要なIstioリソースが異なる。
独自プロトコルの扱い¶
▼ MySQL¶
Istio Ingress Gateway (厳密に言うとGateway) は、独自プロトコル (例:MySQLやRedis以外の非対応プロトコルなど) をTCPプロコトルとして扱う。
そのため、受信した独自プロトコルリクエストにホストヘッダーがあったとしても、これを宛先にフォワーディングできない。
宛先が独自プロトコルリクエストのポート番号だけで宛先 (例:ServiceEntry、外部サーバーなど) を決めてしまう。
03. VirtualService¶
VirtualServiceとは¶
▼ ロードバランサーで使用する場合¶
VirtualServiceは、Istio Ingress Gatewayの一部として、受信した L4/L7 通信をJWTトークンleに紐づくPodへルーティングする。
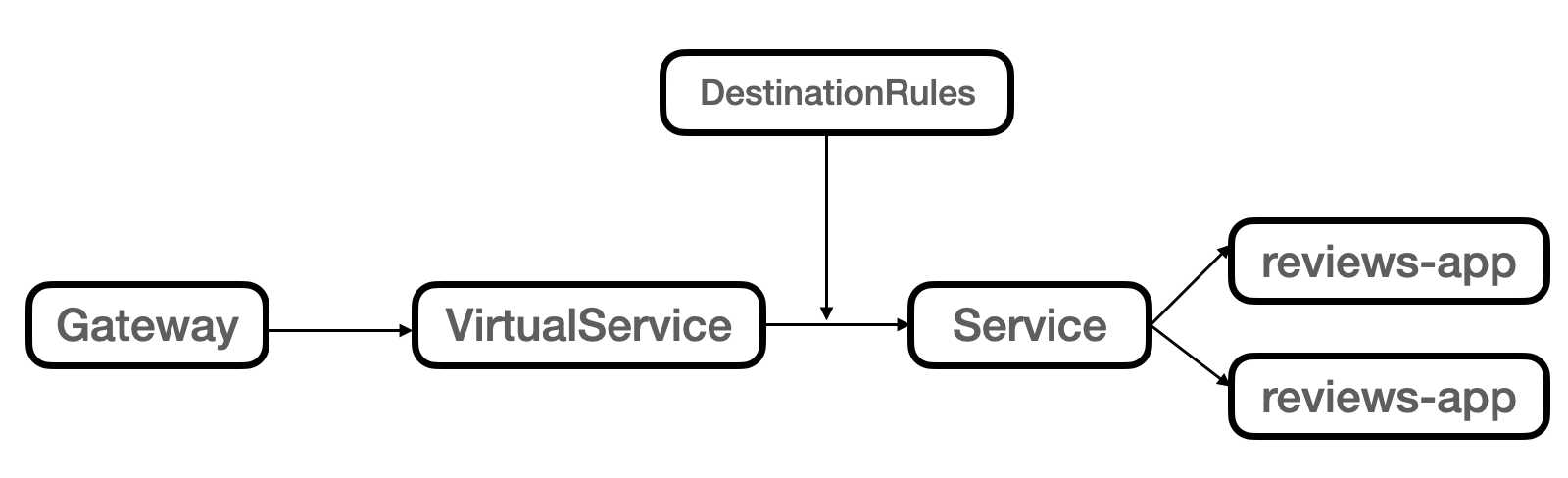
▼ Pod間通信のみで使用する場合¶
VirtualServiceは、宛先Podに紐づくVirtualServiceから情報を取得し、これを宛先とする。
この時、VirtualServiceとDestinationのみを使用する。
Envoyの設定値として¶
▼ リスナーとして¶
Istiodコントロールプレーンは、Gatewayの設定値をEnvoyのリスナーに変換する。
なお、KubernetesのGatewayもEnvoyのリスナーと同等である。
$ kubectl exec \
-it foo-pod \
-n foo-namespace \
-c istio-proxy \
-- bash -c "curl http://127.0.0.1:15000/config_dump?resource={dynamic_listeners}" | yq -P
---
configs:
- "@type": type.googleapis.com/envoy.admin.v3.ListenersConfigDump.DynamicListener
# リスナー
name: 0.0.0.0_50002
active_state:
version_info: 2022-11-24T12:13:05Z/468
listener:
"@type": type.googleapis.com/envoy.config.listener.v3.Listener
name: 0.0.0.0_50002
address:
socket_address:
address: 0.0.0.0
port_value: 50002
# 使用するフィルターを設定する
filter_chains:
- filter_chain_match:
transport_protocol: raw_buffer
application_protocols:
- http/1.1
- h2c
filters:
- name: envoy.filters.network.http_connection_manager
typed_config:
# ネットワークフィルター (http_connection_manager) を指定する
"@type": type.googleapis.com/envoy.extensions.filters.network.http_connection_manager.v3.HttpConnectionManager
stat_prefix: outbound_0.0.0.0_50001
rds:
config_source:
ads: {}
initial_fetch_timeout: 0s
resource_api_version: V3
route_config_name: 50002
...
- "@type": type.googleapis.com/envoy.admin.v3.ListenersConfigDump.DynamicListener
...
▼ ルートとして¶
Istiodコントロールプレーンは、VirtualServiceの設定値をEnvoyのルートに変換する。
$ kubectl exec \
-it foo-pod \
-n foo-namespace \
-c istio-proxy \
-- bash -c "curl http://127.0.0.1:15000/config_dump?resource={dynamic_route_configs}" | yq -P
---
configs:
- "@type": type.googleapis.com/envoy.admin.v3.RoutesConfigDump.DynamicRouteConfig
# ルート
version_info: 2022-11-24T12:13:05Z/468
route_config:
"@type": type.googleapis.com/envoy.config.route.v3.RouteConfiguration
name: 50002
# VirtualService配下のServiceの設定値が変わると、virtual_hostsキーの設定値も変わる
virtual_hosts:
- name: bar-service.bar-namespace.svc.cluster.local:50002
domains:
- bar-service.bar-namespace.svc.cluster.local
- bar-service.bar-namespace.svc.cluster.local:50002
- bar-service
- bar-service:50002
- bar-service.bar-namespace.svc
- bar-service.bar-namespace.svc:50002
- bar-service.bar-namespace
- bar-service.bar-namespace:50002
- 172.16.0.2
- 172.16.0.2:50002
routes:
- match:
prefix: /
route:
cluster: outbound|50002|v1|bar-service.bar-namespace.svc.cluster.local
timeout: 0s
retry_policy:
retry_on: connect-failure,refused-stream,unavailable,cancelled,retriable-status-codes
num_retries: 2
retry_host_predicate:
- name: envoy.retry_host_predicates.previous_hosts
host_selection_retry_max_attempts: "5"
retriable_status_codes:
- 503
max_stream_duration:
max_stream_duration: 0s
grpc_timeout_header_max: 0s
decorator:
operation: bar-service.bar-namespace.svc.cluster.local:50002/*
...
- '@type': type.googleapis.com/envoy.admin.v3.RoutesConfigDump.DynamicRouteConfig
...
つまり、VirtualServiceとJWTトークンleの情報を使用し、Istio Ingress Gatewayで受信した通信とPod間通信の両方を実施する。
クライアント
⬇⬆️︎
envoy
⬇⬆️︎
------------
⬇⬆️︎
envoy # 送信元Envoyからのリクエストをマイクロサービスが受信できるように、リスナーとルートになる
⬇⬆️︎
マイクロサービス
Envoyのリスナーとルートを確認すれば、VirtualServiceの設定が正しく適用できているかを確認できる。
$ istioctl proxy-config routes foo-pod -n foo-namespace
NAME DOMAINS MATCH VIRTUAL SERVICE
50001 foo-service.foo-namespace.svc.cluster.local /* foo-virtual-service.foo-namespace
プラクティス¶
▼ 404 ステータス¶
以下の理由などでVirtualServiceの設定が誤っていると、404 レスポンスを返信する。
- Gatewayで受信した通信の
HostヘッダーとVirtualServiceのそれが合致していない - VirtualServiceの
.spec.exportToキーで.を設定したことにより、Gatewayがルーティング先のVirtualServiceを見つけられない (Istio Ingress Gatewayからリクエストを受信するPodでは要注意)
istioctl proxy-config route コマンドで、Gatewayに紐づくVirtualServiceがいるかを確認できる。
# VirtualServiceが404になっている。
$ istioctl proxy-config route foo-pod
NAME VHOST NAME DOMAINS MATCH VIRTUAL SERVICE
http.50003 blackhole:50003 * /* 404
http.50002 blackhole:50002 * /* 404
http.50001 blackhole:50001 * /* 404
http.50004 blackhole:50004 * /* 404
backend * /stats/prometheus*
backend * /healthz/ready*
▼ 503 ステータス¶
以下の理由などでVirtualServiceの設定が誤っていると、503 レスポンスを返信する。
- VirtualServiceで受信した通信の
HostヘッダーとJWTトークンleのそれが合致していない - JWTトークンleの
.spec.exportToキーで.を設定したことにより、VirtualServiceがルーティング先のJWTトークンleが見つけられない。 (Istio Ingress Gatewayからリクエストを受信するPodでは要注意)
istioctl proxy-config cluster コマンドで、VirtualServiceに紐づくJWTトークンleがいるかを確認できる。
# helloworldでは、紐づくDestinationが見つからない
$ istioctl proxy-config cluster <Pod名>
SERVICE FQDN PORT SUBSET DIRECTION TYPE DESTINATION
helloworld-app-service.services.svc.cluster.local 50002 - outbound EDS
httpbin-app-service.services.svc.cluster.local 50003 - outbound EDS httpbin-app-destination-rule.services
▼ VirtualService数¶
| APIゲートウェイをIstioで管理する場合 | APIゲートウェイをIstioで管理しない場合 | |
|---|---|---|
| VirtualServiceの数 | 外部からのインバウンド通信をAPIゲートウェイにルーティングするVirtualServiceを1つだけ作成しておけばよい。 | APIゲートウェイから全てのマイクロサービスにルーティングできるように、各マイクロサービスにルーティングできるVirtualServiceを定義する必要がある。 |
宛先のServiceのポート番号について¶
Istioは、宛先のServiceに送信しようとするプロトコルを厳格に認識する。
宛先のServiceの .spec.ports[*].name キー (<プロトコル名>-<任意の文字列>) または .spec.ports[*].appProtocol キーを認識し、そのServiceには指定されたプロトコルでしか通信を送れなくなる。
*例*
appProtocolを使用しない場合は以下の通りとなる。
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: foo-service
spec:
ports:
# HTTPプロトコルのみ
- name: http-foo
port: 80
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: foo-service
spec:
ports:
# TCPプロトコルのみ
- name: tcp-foo
port: 9000
*例*
appProtocolを使用する場合は以下の通りとなる。
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: foo-service
spec:
ports:
# HTTPプロトコルのみをVirtualServiceから送信できる
- appProtocol: http
port: 80
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: foo-service
spec:
ports:
# TCPプロトコルのみをVirtualServiceから送信できる
- appProtocol: tcp
port: 9000
04. JWTトークンle¶
JWTトークンleとは¶
▼ ロードバランサーで使用する場合¶
JWTトークンleは、Istio Ingress Gateway (VirtualService + JWTトークンle) で受信した L4/L7 通信を、いずれのPodにルーティングするかを決める。
Istio Ingress Gatewayの実体はPodのため、ロードバランサーというよりは実際はPod間通信で使用していると言える。
Podの宛先情報は、KubernetesのServiceから取得する。
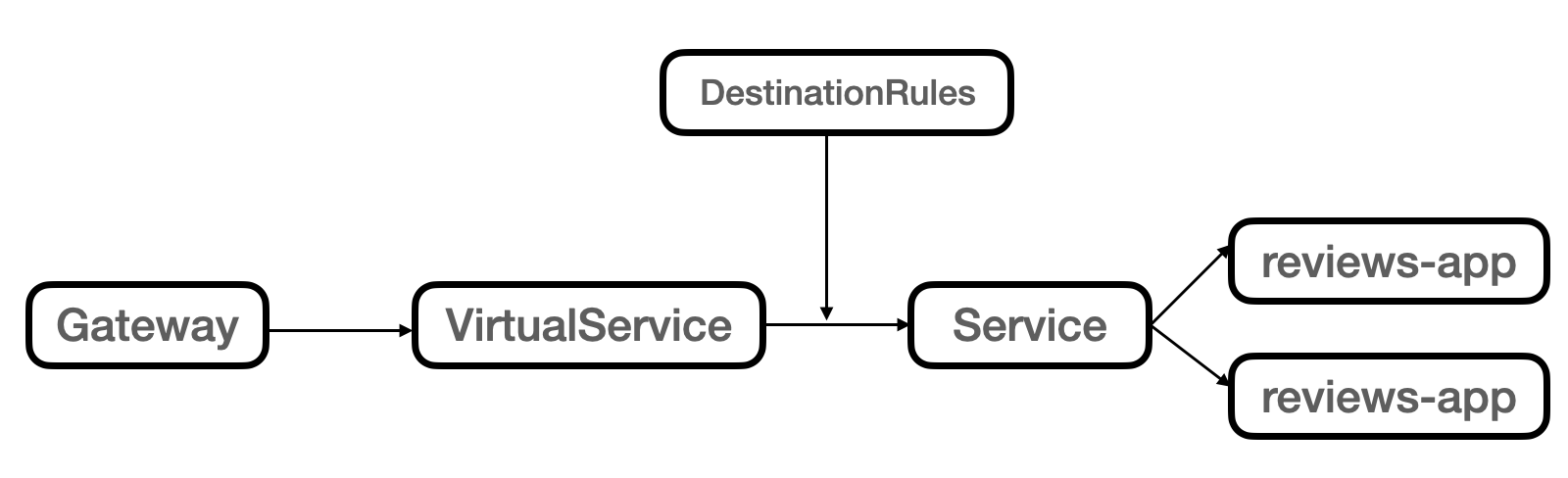
▼ Pod間通信のみで使用する場合¶
JWTトークンleは、VirtualServiceで受信した L4/L7 通信を、いずれのPodにルーティングするかを決める。
Podの宛先情報は、KubernetesのServiceから取得する。
Envoyの設定値として¶
▼ クラスターとして¶
Istiodコントロールプレーンは、JWTトークンleの設定値をEnvoyのクラスターに変換する。
なお、クラスター配下のエンドポイントは、KubernetesのServiceから動的に取得する。
そのため、Envoyのエンドポイントに相当するIstioリソースはない。
$ kubectl exec \
-it foo-pod \
-n foo-namespace \
-c istio-proxy \
-- bash -c "curl http://127.0.0.1:15000/config_dump?resource={dynamic_active_clusters}" | yq -P
---
configs:
- "@type": type.googleapis.com/envoy.admin.v3.ClustersConfigDump.DynamicCluster
# クラスター
version_info: 2022-11-24T12:13:05Z/468
cluster:
"@type": type.googleapis.com/envoy.config.cluster.v3.Cluster
name: outbound|50002|v1|bar-service.bar-namespace.svc.cluster.local
type: EDS
eds_cluster_config:
eds_config:
ads: {}
initial_fetch_timeout: 0s
resource_api_version: V3
service_name: outbound|50002|v1|bar-service.bar-namespace.svc.cluster.local
...
- "@type": type.googleapis.com/envoy.admin.v3.ClustersConfigDump.DynamicCluster
...
$ kubectl exec \
-it foo-pod \
-n foo-namespace \
-c istio-proxy \
-- bash -c "curl http://127.0.0.1:15000/config_dump?include_eds" | yq -P
---
configs:
# エンドポイント
dynamic_endpoint_configs:
- endpoint_config:
"@type": type.googleapis.com/envoy.config.endpoint.v3.ClusterLoadAssignment
cluster_name: outbound|50002|v1|bar-service.bar-namespace.svc.cluster.local
# いずれかのエンドポイントにロードバランシング
endpoints:
- locality:
region: ap-northeast-1
zone: ap-northeast-1a
lb_endpoints:
- endpoint:
address:
socket_address:
address: 11.0.0.1
port_value: 80
health_check_config: {}
health_status: HEALTHY
metadata:
filter_metadata:
istio:
workload: bar
envoy.transport_socket_match:
tlsMode: istio
load_balancing_weight: 1
- locality:
region: ap-northeast-1
zone: ap-northeast-1d
lb_endpoints:
- endpoint:
address:
socket_address:
address: 11.0.0.2
port_value: 80
health_check_config: {}
health_status: HEALTHY
metadata:
filter_metadata:
istio:
workload: bar
envoy.transport_socket_match:
tlsMode: istio
load_balancing_weight: 1
- locality:
region: ap-northeast-1
zone: ap-northeast-1d
lb_endpoints:
- endpoint:
address:
socket_address:
address: 11.0.0.3
port_value: 80
health_check_config: {}
health_status: HEALTHY
metadata:
filter_metadata:
istio:
workload: baz
envoy.transport_socket_match:
tlsMode: istio
load_balancing_weight: 1
policy:
overprovisioning_factor: 140
...
- endpoint_config:
...
つまり、VirtualServiceとJWTトークンleの情報を使用し、Istio Ingress Gatewayで受信した通信とPod間通信の両方を実施する。
Pod間通信時には、VirtualServiceとDestinationのみを使用する。
クライアント
⬇⬆️︎
envoy
⬇⬆️︎
------------
⬇⬆️︎
envoy # 送信元Envoyからのリクエストをマイクロサービスが受信できるように、クラスターとエンドポイントになる
⬇⬆️︎
マイクロサービス
Envoyのクラスターとエンドポイントを確認すれば、JWTトークンleの設定が正しく適用できているかを確認できる。
$ istioctl proxy-config cluster foo-pod -n foo-namespace
SERVICE FQDN PORT SUBSET DIRECTION TYPE DESTINATION RULE
<Serviceの完全修飾ドメイン名> <Serviceが待ち受けるポート番号> <サブセット名> <通信の方向> <ディスカバリータイプ> <JWTトークンle名>.<Namespace名>
foo-service.foo-namespace.svc.cluster.local 50001 v1 outbound EDS foo-destination-rule.foo-namespace
bar-service.bar-namespace.svc.cluster.local 50002 v1 outbound EDS bar-destination-rule.bar-namespace
baz-service.baz-namespace.svc.cluster.local 50003 v1 outbound EDS baz-destination-rule.baz-namespace
05. ServiceEntry¶
ServiceEntryとは¶
ServiceEntryは、クラスター外のドメイン名などを登録する。
Istiov1.3 より前は、ConfigMapのデフォルトが REGISTRY_ONLY になっていた。このため、ServiceEntryでマイクロサービスを登録しない限り、サービスメッシュ外部と通信できなかった。
しかし、v1.3 以降、ServiceEntryでマイクロサービスを登録しなくても、サービスメッシュ外部の任意のマイクロサービスと通信できるようになった。
ただし、登録しない限り、マイクロサービスを個別に認識できず、すべて PassthroughCluster として扱う。
類似するExternalName Serviceでも同じことを実現できるが、Istioの機能を使用できない。
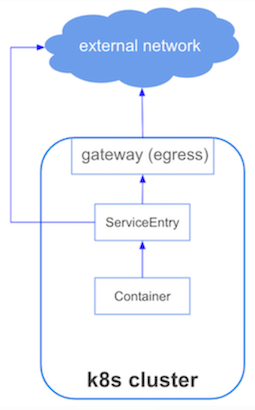
メッシュ外とクラスター内Podとの通信¶
ServiceEntryは、クラスター外の宛先をサービスメッシュに登録する。
クラスター内の宛先の場合、クラスター内のPodでサービスメッシュ外のKubernetes Serviceを指定する。
06. Sidecar¶
Sidecarとは¶
istio-proxyに最初限のネットワーク設定を適用する。
デフォルトでは、サービスメッシュに登録した全てのPod間が通信できる。
Sidecarを使用すると、指定した設定以外の通信を除去し、特定のPod間でのみ通信できるようになる。
ServiceEntryと同時に必要なリソース¶
▼ Istio Egress Gateway¶
ServiceEntryには、Istio Egress Gatewayが必須ではない。
ただし、Istio Egress Gatewayを使用しないと、マイクロサービスからistio-proxyコンテナを経由せず、外部システムに直接HTTPSリクエストを送信できるようになってしまう。
そのため、システムの安全性が低くなる。
▼ ServiceEntryの前段のJWTトークンle¶
ServiceEntryから外部にHTTPリクエストを送信する場合、JWTトークンleは不要である。
しかし、ServiceEntryから宛先にHTTPリクエストを送信する場合、JWTトークンleは不要である。
06. EnvoyFilter¶
ネットワークフィルター¶
▼ network.http_connection_manager をマッチ対象とする場合¶
network.http_connection_manager をマッチ対象として、フィルターを変更する。
例えば、Istioの v1.17.5 のistio-proxyのフィルターの設定値を変更する。
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: EnvoyFilter
metadata:
labels:
istio.io/rev: 1-17-5
name: stats-filter-1.17-1-17-5
namespace: istio-system
spec:
configPatches:
# ネットワークフィルターであるhttp_connection_managerの設定値を変更する
- applyTo: HTTP_FILTER
match:
# istio-proxyコンテナのアウトバウンド通信 (Egressリスナー後フィルター)
context: SIDECAR_OUTBOUND
listener:
filterChain:
filter:
name: envoy.filters.network.http_connection_manager
subFilter:
# マッチ対象のHTTPフィルターを指定する
name: envoy.filters.http.router
proxy:
# istio-proxyコンテナが1.17系の場合のみ
proxyVersion: ^1\.17.*
patch:
# http_connection_managerの直前に指定したフィルターを挿入する
operation: INSERT_BEFORE
value:
name: istio.stats
typed_config:
"@type": type.googleapis.com/udpa.type.v1.TypedStruct
type_url: type.googleapis.com/stats.PluginConfig
value: {}
# ネットワークフィルターであるhttp_connection_managerの設定値を変更する
- applyTo: HTTP_FILTER
match:
# istio-proxyコンテナのインバウンド通信 (Ingressリスナー後フィルター)
context: SIDECAR_INBOUND
listener:
filterChain:
filter:
name: envoy.filters.network.http_connection_manager
subFilter:
# マッチ対象のHTTPフィルターを指定する
name: envoy.filters.http.router
proxy:
# istio-proxyコンテナが1.17系の場合のみ
proxyVersion: ^1\.17.*
patch:
# http_connection_managerの直前に指定したフィルターを挿入する
operation: INSERT_BEFORE
value:
name: istio.stats
typed_config:
"@type": type.googleapis.com/udpa.type.v1.TypedStruct
type_url: type.googleapis.com/stats.PluginConfig
value:
disable_host_header_fallback: "true"
# ネットワークフィルターであるhttp_connection_managerの設定値を変更する
- applyTo: HTTP_FILTER
match:
# istio-ingressgateway内のistio-proxyコンテナ
context: GATEWAY
listener:
filterChain:
filter:
name: envoy.filters.network.http_connection_manager
subFilter:
# マッチ対象のHTTPフィルターを指定する
name: envoy.filters.http.router
proxy:
# istio-proxyコンテナが1.17系の場合のみ
proxyVersion: ^1\.17.*
patch:
# http_connection_managerの直前に指定したフィルターを挿入する
operation: INSERT_BEFORE
value:
name: istio.stats
typed_config:
"@type": type.googleapis.com/udpa.type.v1.TypedStruct
type_url: type.googleapis.com/stats.PluginConfig
value:
disable_host_header_fallback: "true"
# デフォルトのフィルターよりも先に適用する
priority: -1
▼ network.tcp_proxy をマッチ対象とする場合¶
network.tcp_proxy をマッチ対象として、フィルターを変更する。
例えば、Istioの v1.17.5 のistio-proxyのフィルターの設定値を変更する。
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: EnvoyFilter
metadata:
labels:
istio.io/rev: 1-17-5
name: tcp-stats-filter-1.17-1-17-5
namespace: istio-system
spec:
configPatches:
# ネットワークフィルターの設定値を変更する
- applyTo: NETWORK_FILTER
match:
# istio-proxyコンテナのインバウンド通信 (Ingressリスナー後のフィルター)
context: SIDECAR_INBOUND
listener:
filterChain:
filter:
# マッチ対象のネットワークフィルターを指定する
name: envoy.filters.network.tcp_proxy
proxy:
# istio-proxyコンテナが1.17系の場合のみ
proxyVersion: ^1\.17.*
patch:
# tcp_proxyの直前に指定したフィルターを挿入する
operation: INSERT_BEFORE
value:
name: istio.stats
typed_config:
"@type": type.googleapis.com/udpa.type.v1.TypedStruct
type_url: type.googleapis.com/stats.PluginConfig
value: {}
# ネットワークフィルターの設定値を変更する
- applyTo: NETWORK_FILTER
match:
# istio-proxyコンテナのアウトバウンド通信 (Egressリスナー後のフィルター)
context: SIDECAR_OUTBOUND
listener:
filterChain:
filter:
# マッチ対象のネットワークフィルターを指定する
name: envoy.filters.network.tcp_proxy
proxy:
# istio-proxyコンテナが1.17系の場合のみ
proxyVersion: ^1\.17.*
patch:
# tcp_proxyの直前に指定したフィルターを挿入する
operation: INSERT_BEFORE
value:
name: istio.stats
typed_config:
"@type": type.googleapis.com/udpa.type.v1.TypedStruct
type_url: type.googleapis.com/stats.PluginConfig
value: {}
# ネットワークフィルターの設定値を変更する
- applyTo: NETWORK_FILTER
match:
# istio-ingressgateway内のistio-proxyコンテナ
context: GATEWAY
listener:
filterChain:
filter:
# マッチ対象のネットワークフィルターを指定する
name: envoy.filters.network.tcp_proxy
proxy:
# istio-proxyコンテナが1.17系の場合のみ
proxyVersion: ^1\.17.*
patch:
# tcp_proxyの直前に指定したフィルターを挿入する
operation: INSERT_BEFORE
value:
name: istio.stats
typed_config:
"@type": type.googleapis.com/udpa.type.v1.TypedStruct
type_url: type.googleapis.com/stats.PluginConfig
value: {}
# デフォルトのフィルターよりも先に適用する
priority: -1
07. PeerAuthentication¶
Pod間通信時、相互TLS認証を実施する。
08. RequestAuthenticationとAuthorizationPolicy¶
RequestAuthenticationとAuthorizationPolicyとは¶
Pod間通信時、JWTによる認証と認可を実施する。
JWTトークンが失効/不正な場合、RequestAuthenticationは 401 レスポンスを返信する。
JWTトークンがない場合、AuthorizationPolicyは 403 レスポンスを返信する必要がある。
なお、RequestAuthenticationを使用せずにマイクロサービスで同様の実装をしても良い。
また、Nginx製のBFFなど、認証処理を実装しにくい場所にのみ採用しても良い。
Auth0に送信する場合¶
注意点として、そもそもリクエストにJWTトークンが含まれていない場合には認証処理をスキップできてしまう。
代わりに、JWTトークンが含まれていないリクエストをAuthorizationPolicyによる認可処理失敗 (403 ステータス) として扱う必要がある。
Auth0 (クラウドのためサービスメッシュ外にある) の宛先情報をIstioに登録する必要があるため、Istio Egress GatewayやServiceEntry経由で接続できるようにする。
apiVersion: security.istio.io/v1
kind: RequestAuthentication
metadata:
name: foo-request-authentication-jwt
spec:
jwtRules:
# JWTトークンの発行元IDプロバイダーの識別子を設定する
# ブラウザから接続する
- issuer: https://<Auth0のドメイン>/
# IDプロバイダーのJWKsエンドポイントを設定し、アクセストークン署名検証のための公開鍵を取得する
jwksUri: https://<Auth0のドメイン>/.well-known/jwks.json
# 既存のJWTを再利用し、宛先マイクロサービスにそのままフォワーディングする
forwardOriginalToken: true
# Authorizationヘッダーを指定する
fromHeaders:
- name: Authorization
prefix: "Bearer "
---
# AuthorizationPolicyでRequestAuthenticationを強制する
apiVersion: security.istio.io/v1
kind: AuthorizationPolicy
metadata:
name: foo-authorization-policy
spec:
# 許可する
action: ALLOW
rules:
- when:
- key: request.auth.claims[iss]
# JWTトークンがある場合にのみ許可する
values: ["https://<Auth0のドメイン>/"]
Keycloakに送信する場合¶
注意点として、そもそもリクエストにJWTが含まれていない場合には認証処理をスキップできてしまう。
代わりに、JWTが含まれていないリクエストをAuthorizationPolicyによる認可処理失敗 (403 ステータス) として扱う必要がある。
Keycloakの宛先情報をIstioに登録する必要があるため、これのPodをサービスメッシュ内に配置するか、サービスメッシュ外に配置してIstio Egress GatewayやServiceEntry経由で接続できるようにする。
apiVersion: security.istio.io/v1
kind: RequestAuthentication
metadata:
name: foo-request-authentication-jwt
spec:
jwtRules:
# JWTトークンの発行元IDプロバイダーの識別子を設定する
# ブラウザから接続する
- issuer: http://keycloak.com/realms/<realm名>
# IDプロバイダーのJWKsエンドポイントを設定し、アクセストークン署名検証のための公開鍵を取得する
# ブラウザから、またはAPIに直接接続する
jwksUri: http://keycloak.foo-namespace.svc.cluster.local/realms/<realm名>/protocol/openid-connect/certs
# 既存のJWTを再利用し、宛先マイクロサービスにそのままフォワーディングする
forwardOriginalToken: true
# Authorizationヘッダーを指定する
fromHeaders:
- name: Authorization
prefix: "Bearer "
---
# RequestAuthenticationで設定したAuthorizationヘッダーがない場合には認可エラーとする
apiVersion: security.istio.io/v1
kind: AuthorizationPolicy
metadata:
name: foo-authorization-policy
spec:
# 許可する
action: ALLOW
rules:
- when:
- key: request.auth.claims[iss]
# JWTトークンがある場合にのみ許可する
values:
["http://keycloak.foo-namespace.svc.cluster.local/realms/<realm名>"]
OAuth2 Proxyを介してKeycloakに送信する場合¶
注意点として、そもそもリクエストにJWTが含まれていない場合には認証処理をスキップできてしまう。
代わりに、JWTが含まれていないリクエストをAuthorizationPolicyによる認可処理失敗 (403 ステータス) として扱う必要がある。
OAuth2 Proxyの宛先情報をIstioに登録する必要があるため、これのPodをサービスメッシュ内に配置するか、サービスメッシュ外に配置してIstio Egress GatewayやServiceEntry経由で接続できるようにする。
apiVersion: security.istio.io/v1
kind: RequestAuthentication
metadata:
name: foo-request-authentication-jwt
spec:
jwtRules:
# JWTトークンの発行元IDプロバイダーの識別子を設定する
# ブラウザから接続する
- issuer: http://oauth2-proxy.com/realms/<realm名>
# IDプロバイダーのJWKsエンドポイントを設定し、アクセストークン署名検証のための公開鍵を取得する
# ブラウザから、またはAPIに直接接続する
jwksUri: http://oauth2-proxy.foo-namespace.svc.cluster.local/realms/<realm名>/protocol/openid-connect/certs
# 既存のJWTを再利用し、宛先マイクロサービスにそのままフォワーディングする
forwardOriginalToken: true
# Authorizationヘッダーを指定する
fromHeaders:
- name: Authorization
prefix: "Bearer "
---
# RequestAuthenticationで設定したAuthorizationヘッダーがない場合には認可エラーとする
apiVersion: security.istio.io/v1
kind: AuthorizationPolicy
metadata:
name: foo-authorization-policy
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: istio-ingressgateway
action: CUSTOM
# oauth2-proxyプロバイダーの設定を使用する
provider:
name: oauth2-proxy
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: foo-cm
data:
mesh: |
extensionProviders:
- name: oauth2-proxy
envoyExtAuthzHttp:
# 認可リクエストの宛先を設定する
service: oauth2-proxy.foo-namespace.svc.cluster.local
port: 4180
# 認可リクエストに追加する必要のあるヘッダーを設定する
includeRequestHeadersInCheck:
- cookie
# 認証の完了後に、元の宛先へのリクエストを変更するかどうかを設定する
# リフレッシュしたアクセストークンを元のAuthorizarionヘッダーに設定したい場合、これを設定する必要がある (たぶん)
headersToUpstreamOnAllow:
- authorization
headersToDownstreamOnDeny:
- set-cookie
09. 環境変数¶
設定によっては、リソースではなくpilot-agentの環境変数として直接的に渡す必要がある。
これらの環境変数は、いずれistio-sidecar-injector (ConfigMap) やistio-mesh-cm (ConfigMap) などに移行される可能性がある。
| 環境変数 | 対応する設定 (実験段階) |
|---|---|
ENHANCED_RESOURCE_SCOPING |
istio-mesh-cm (ConfigMap) で、discoverySelectors を有効化してもよい。 |
ENABLE_NATIVE_SIDECARS |
istio-sidecar-injector (ConfigMap) で、istio-proxyの代わりにKubernetesのInit Container |
ENABLE_RESOLUTION_NONE_TARGET_PORT |
|
ENABLE_DELIMITED_STATS_TAG_REGEX |
|
PREFER_JWTトークンLE_TLS_FOR_EXTERNAL_SERVICES |
|
ENABLE_ENHANCED_JWTトークンLE_MERGE |
|
PILOT_UNIFIED_SIDECAR_SCOPE |
|
VERIFY_CERT_AT_CLIENT |
どこにこの変数あるんやろか... |